JUC并发编程上篇
JUC上篇
1.大纲
2.进程与线程
本章内容
- 进程和线程的概念
- 并行和并发的概念
- 线程基本应用
2.1进程与线程
进程:
- 一个程序被运行,从磁盘加载这个程序的代码到内存,就开起了一个进程。
- 进程可以视为程序的一个实例,大部分程序可以同时运行多个实例进程(笔记本,记事本,图画,浏览器等),也有的程序只能启动一个实例进程(网易云音乐,360安全卫士等)。
线程:
- 一个进程内可以分为一到多个线程。
- 一个线程就是一个指令流,将指令流中的一条条指令以一定的顺序交给CPU执行。
- Java中线程是最小调度单元,进程作为资源分配的最小单位。在windows中进程是不活动的,仅仅作为线程的容器。
二者对比
- 进程基本上相互独立的,而线程存在于进程内,是进程的一个子集
- 进程拥有共享的资源,如内存空间等,供其内部的线程共享
- 进程间通信较为复杂
- 同一台计算机的进程通信称为 IPC(Inter-process communication)
- 不同计算机之间的进程通信,需要通过网络,并遵守共同的协议,例如 HTTP
- 线程通信相对简单,因为它们共享进程内的内存,一个例子是多个线程可以访问同一个共享变量
- 线程更轻量,线程上下文切换成本一般上要比进程上下文切换低
小结:
| 分类 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 进程定义 | 程序被运行时,从磁盘加载代码到内存,形成一个进程。进程是程序的一个实例。 |
| 进程示例 | 多实例:记事本、图画、浏览器单实例:网易云音乐、360安全卫士 |
| 线程定义 | 一个进程可以包含一个或多个线程;线程是指令流的执行单元,按照顺序将指令交给 CPU 执行。 |
| Java 中的特点 | Java 中线程是最小调度单元,进程是资源分配的最小单位。在 Windows 中,进程本身是不活动的,仅作为线程的容器。 |
| 对比项 | 进程 | 线程 |
|---|---|---|
| 所属关系 | 独立存在 | 存在于进程内部,是其子集 |
| 资源共享 | 拥有自己的资源;同一进程内线程共享进程资源(如内存) | 共享进程资源(如变量、堆内存) |
| 通信复杂度 | 进程间通信较复杂,需要 IPC 或网络协议(如 HTTP) | 通信简单,可直接通过共享内存通信 |
| 上下文切换成本 | 较高 | 较低,线程更轻量 |
2.2 并行与并发
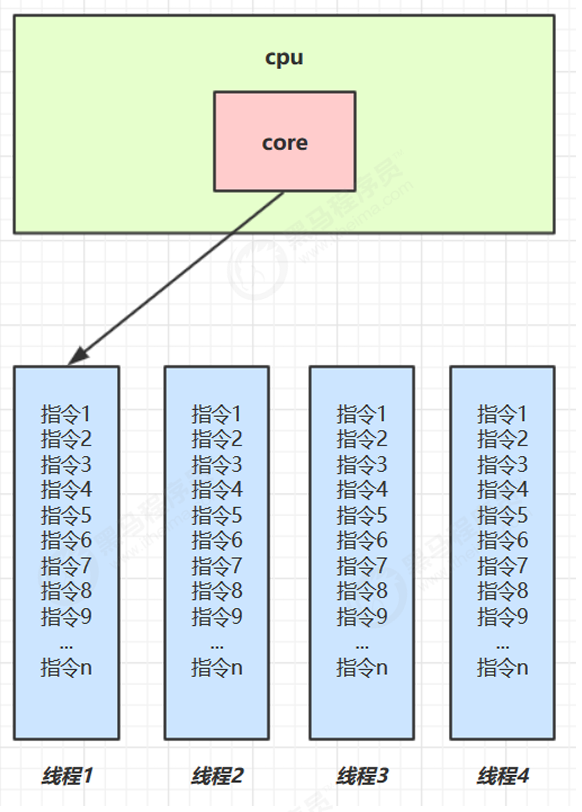
操作系统任务调度器,可以把CPU时间交给不同线程使用,线程可以轮流使用CPU资源。
- 单核 cpu 下,线程实际还是 串行执行 的。操作系统中有一个组件叫做任务调度器,将 cpu 的时间片(windows下时间片最小约为 15 毫秒)分给不同的程序使用,只是由于 cpu 在线程间(时间片很短)的切换非常快,人类感觉是 同时运行的 。总结为一句话就是:微观串行,宏观并行,
一般会将这种 线程轮流使用 CPU 的做法称为并发, concurrent - 多核 cpu下,每个核(core) 都可以调度运行线程,这时候线程可以是并行的。
并发并行:
- 并行:在同一时刻,有多个指令在多个 CPU 上同时执行 同一时间同时做多件事情的能力。多个人做多件事。
- 并发:在同一时刻,有多个指令在单个 CPU 上交替执行 同一时间段处理多件事情的能力。一个人做多件事。
2.3线程应用
2.3.1异步调用
同步异步:
- 需要等待结果返回,才能继续运行就是同步
- 不需要等待结果返回,就能继续运行就是异步
多线程可以让方法执行变为异步的,不会干巴巴等着,比如读取磁盘要花费5秒,如果没有线程调度机制,这5秒什么事情都做不了。
视频文件要转换格式操作比较费时,可以开一个新线程处理视频转换,避免阻塞主线程。
2.3.2 提升效率

2.3.3线程应用提升效率验证和小结
- 单核 cpu 下,多线程不能实际提高程序运行效率,只是为了能够在不同的任务之间切换,不同线程轮流使用cpu ,不至于一个线程总占用 cpu,别的线程没法干活
- 多核 cpu 可以并行跑多个线程,但能否提高程序运行效率还是要分情况的
有些任务,经过精心设计,将任务拆分,并行执行,当然可以提高程序的运行效率。但不是所有计算任务都能拆分(参考后文的【阿姆达尔定律】) 也不是所有任务都需要拆分,任务的目的如果不同,谈拆分和效率没啥意义 - IO 操作不占用 cpu,只是我们一般拷贝文件使用的是【阻塞 IO】,这时相当于线程虽然不用 cpu,但需要一直等待 IO 结束,没能充分利用线程。所以才有后面的【非阻塞 IO】和【异步 IO】优化
3.Java 线程
本章内容
- 创建和运行线程
- 查看线程
- 线程 API
- 线程状态
3.1 创建和运行线程
方法一,直接使用 Thread
Thread 创建线程方式:创建线程类,匿名内部类方式
- start() 方法底层其实是给 CPU 注册当前线程,并且触发 run() 方法执行
- 线程的启动必须调用 start() 方法,如果线程直接调用 run() 方法,相当于变成了普通类的执行,此时主线程将只有执行该线程
- 建议线程先创建子线程,主线程的任务放在之后,否则主线程(main)永远是先执行完
Thread 构造器:
public Thread()public Thread(String name)
1 | // 创建线程对象 |
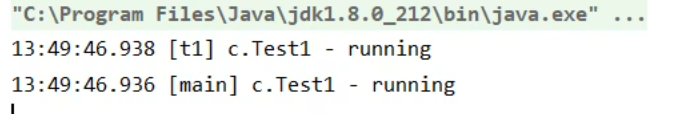
例如:
1 | (topic = "c.Test1") |

方法二,使用Runnable配合Thread创建线程
Runnable 创建线程方式:创建线程类,匿名内部类方式
Thread 的构造器:
public Thread(Runnable target)public Thread(Runnable target, String name)
把【线程】和【任务】(要执行的代码)分开
- Thread 代表线程
- Runnable 可运行的任务(线程要执行的代码)
1 | Runnable runnable = new Runnable() { |
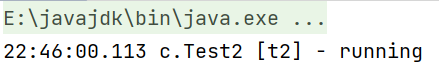
例如:
1 | (topic="c.Test2") |
JDK8后可以用lambda简化
1 |
|
还可以再简化:

将任务和线程分离:

原理之 Thread 与 Runnable 的关系
1 | public class ThreadDemo { |
Thread 类本身也是实现了 Runnable 接口,Thread 类中持有 Runnable 的属性,执行线程 run 方法底层是调用 Runnable#run:
1 | public class Thread implements Runnable { |
Thread本身实现了Runnable接口。Thread中持有一个Runnable target对象。- 当我们使用
new Thread(runnable)创建线程时,真正运行的是runnable.run()。 - 若没有传入 target,则可以重写 Thread 的 run 方法。
小结
- 方法1(直接使用 Thread) 是把线程和任务合并在了一起,方法2(使用Runnable配合Thread创建线程) 是把线程和任务分开了
- 用 Runnable 更容易与线程池等高级 API 配合
- 用 Runnable 让任务类脱离了 Thread 继承体系,更灵活
| 方法 | 描述 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| 方式一:继承 Thread 类 | 任务和线程绑定在一起 | 不灵活,无法复用任务 |
| 方式二:实现 Runnable 接口 | 任务与线程分离 | 更加灵活,任务可以被多个线程复用;更适合配合线程池等高级 API |
为什么推荐使用 Runnable?
- 任务解耦:Runnable 让“线程的创建”与“任务的逻辑”分离,职责更清晰。
- 复用性强:一个
Runnable实例可以被多个线程执行。 - 兼容性好:避免 Java 单继承限制,可以让任务类继承其他类。
- 线程池支持:线程池的核心工作单元就是
Runnable或Callable。
方法三,FutureTask 配合 Thread
适用场景
当你希望线程执行后能返回一个结果,就不能使用 Runnable,而应该使用 Callable + FutureTask,FutureTask 能够接收 Callable 类型的参数,用来处理有返回结果的情况
原理说明
FutureTask实现了Runnable接口,所以可以被Thread执行。FutureTask
也是一个“任务对象”,支持:
run():用于被线程调用执行get():用于获取线程执行完后的结果(阻塞方法,等待执行完毕)
1 | public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V> { |
| 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|
| 支持任务执行后返回结果 | 编码略复杂(相比 Runnable) |
| 支持异常抛出和捕获 | 使用时需注意 get() 阻塞特性 |
可以用于线程同步(get() 阻塞等待) |
线程执行顺序不可控(需结合线程池优化) |
| 实现步骤 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 定义一个类,实现 Callable<V> 接口,指定返回值类型 |
| 2 | 实现 call() 方法,编写线程执行的逻辑(可直接返回结果) |
| 3 | 创建该 Callable 实例 |
| 4 | 使用 FutureTask 将 Callable 包装成一个“未来任务对象” |
| 5 | 使用 Thread 将 FutureTask 包装成线程 |
| 6 | 启动线程,并通过 get() 获取执行结果(会阻塞) |
1 |
|
小结:FutureTask 是连接 Callable 和 Thread 的桥梁,它把“能返回结果的任务”交给线程执行,并允许我们在主线程中同步等待结果。
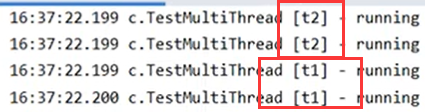
3.2观察多个线程同时运行时线程运行现象
主要是理解
- 交替执行
- 谁先谁后,不由我们控制,由底层任务调度器决定
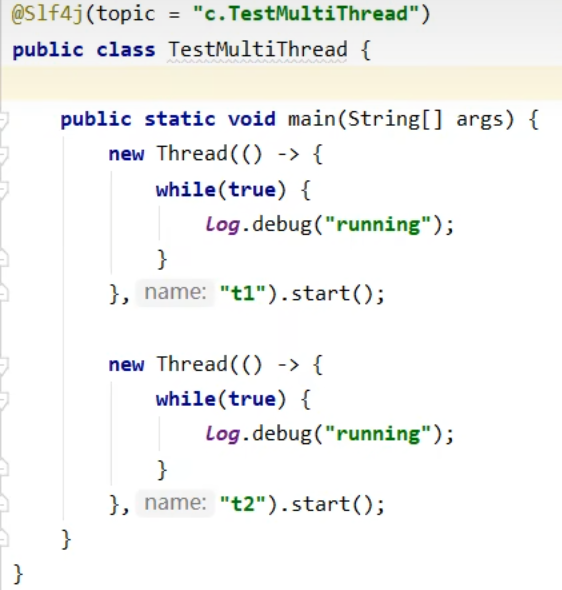
交替运行。
3.3查看进程线程的方法
windows
查看方式:1.通过任务管理器。2.在控制台输入tasklist
找到java进程:
1 | tasklist | findstr java |
查看所有java进程:
1 | jps |
杀死某个进程:
1 | taskkill /F /PID PID号 |
linux
- ps -fe 查看所有进程
- ps -fT -p
查看某个进程(PID)的所有线程 - kill 杀死进程
- top 按大写 H 切换是否显示线程
- top -H -p
查看某个进程(PID)的所有线程
Java
- jps 命令查看所有 Java 进程
- jstack 查看某个 Java 进程(PID)的所有线程状态
- jconsole 来查看某个 Java 进程中线程的运行情况(图形界面)
jconsole的使用

3.4原理之线程运行
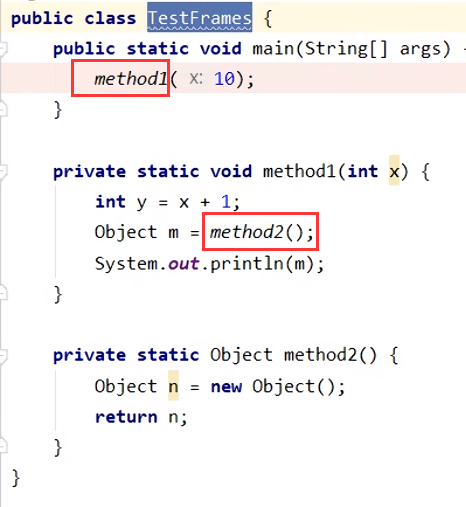
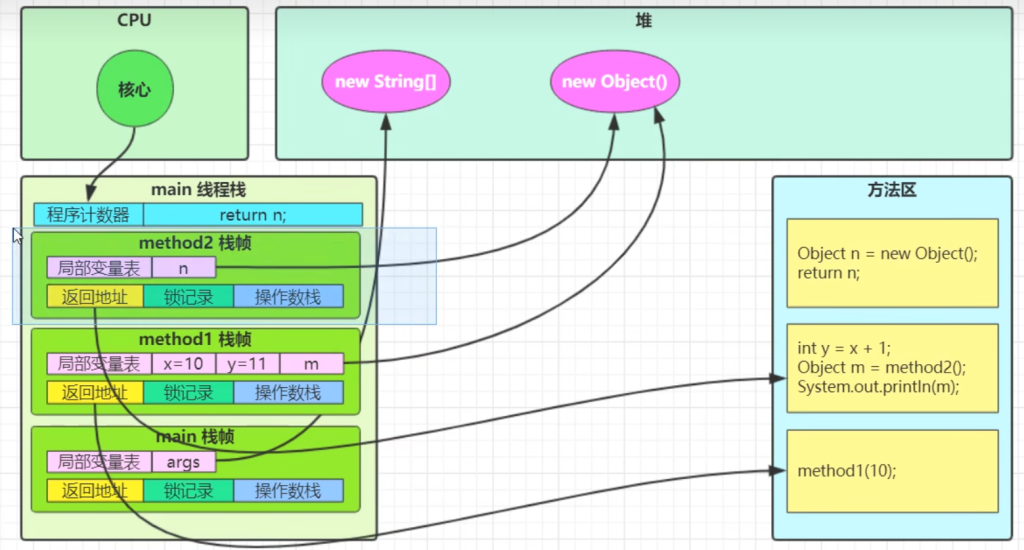
栈与栈帧(详情见JVM基础篇)
JVM由堆、栈、方法区组成。栈内存是给线程用的,每个线程启动后,虚拟机会为其分配一块栈内存。
栈由栈帧组成,对应每次方法调用时所占用的内存。
每个线程只能有一个活动栈帧,对应着当前正在执行的那个方法。
栈帧图解
Java 虚拟机栈的栈帧中主要包含三方面的内容:
- 局部变量表:作用是在运行过程中存放所有的局部变量。
- 操作数栈:是栈帧中虚拟机在执行指令过程中用来存放临时数据的一块区域。
- 帧数据:包含动态链接、方法出口、异常表的引用。
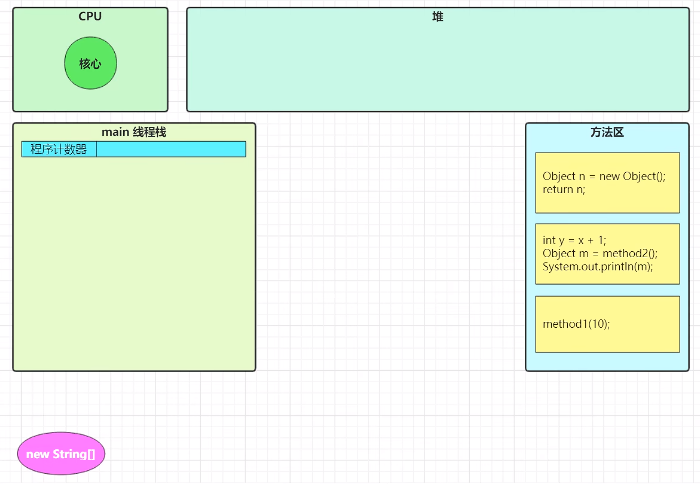
返回地址对应的是方法区中的方法,局部变量对应的是堆中的对象。
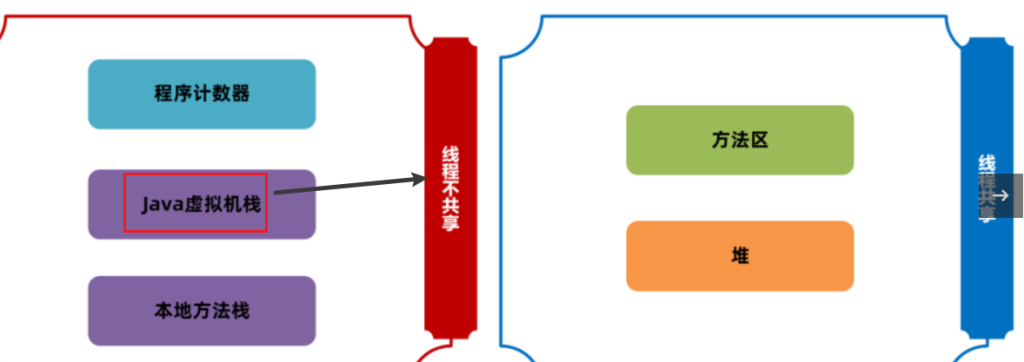
3.5线程运行原理-多线程
线程的栈内存相互独立的,每个线程拥有自己的独立的栈内存,里面有很多个栈帧
究其原因就是虚拟机栈是线程私有的
具体见JVM基础篇
3.6线程上下文切换(Thread Context Switch)
CPU不再执行当前的线程,转而执行另一个线程的代码原因可能有:
1.线程的CPU时间片用完。
2.垃圾回收。暂停当前所有的工作线程,让垃圾回收的线程去回收垃圾。
3.有更高优先级的线程需要运行。
4.线程自己调用了sleep,yield,wait,join,park,synchronized,lock等方法。
当线程上下文切换发生时,需要由操作系统保存当前线程的状态,并恢复另一个线程的状态,Java 中对应的概念就是程序计数器(Program Counter Register),它的作用是记住下一条 jvm 指令的执行地址,是线程私有的
- 状态包括程序计数器、虚拟机栈中每个栈帧的信息,如局部变量、操作数栈、返回地址等
- Context Switch 频繁发生会影响性能
3.7常见方法
3.7.1相关API
Thread 类 API:
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public void start() | 启动一个新线程,Java虚拟机调用此线程的 run 方法 |
| public void run() | 线程启动后调用该方法 |
| public void setName(String name) | 给当前线程取名字 |
| public void getName() | 获取当前线程的名字 线程存在默认名称:子线程是 Thread-索引,主线程是 main |
| public static Thread currentThread() | 获取当前线程对象,代码在哪个线程中执行 |
| public static void sleep(long time) | 让当前线程休眠多少毫秒再继续执行 Thread.sleep(0) : 让操作系统立刻重新进行一次 CPU 竞争 |
| public static native void yield() | 提示线程调度器让出当前线程对 CPU 的使用 |
| public final int getPriority() | 返回此线程的优先级 |
| public final void setPriority(int priority) | 更改此线程的优先级,常用 1 5 10 |
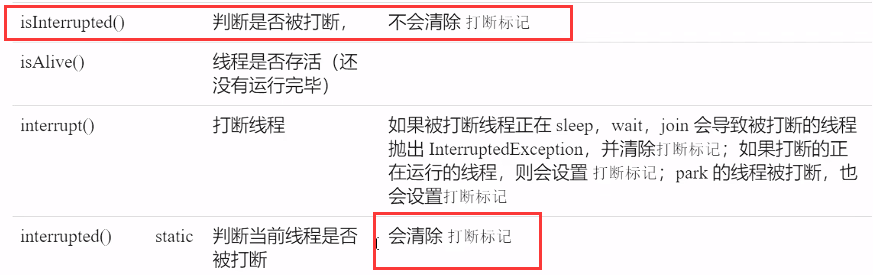
| public void interrupt() | 中断这个线程,异常处理机制 |
| public static boolean interrupted() | 判断当前线程是否被打断,清除打断标记 |
| public boolean isInterrupted() | 判断当前线程是否被打断,不清除打断标记 |
| public final void join() | 等待这个线程结束 |
| public final void join(long millis) | 等待这个线程死亡 millis 毫秒,0 意味着永远等待 |
| public final native boolean isAlive() | 线程是否存活(还没有运行完毕) |
| public final void setDaemon(boolean on) | 将此线程标记为守护线程或用户线程 |
- start() 启动一个新线程,在新的线程运行run方法中的代码。start方法只能让线程进入就绪,代码不一定立即执行(只有等CPU的时间片分配给它才能运行)。每个线程对象的start方法只能调用一次。
- join()等待线程运行结束。假如当前的主线程正在等待某个线程执行结束后返回的结果,就可以调用这个join方法。join(long n)表示最多等待n毫秒。
- getId()获得线程id,getName()获得线程名称,setName()设置线程名称,getPriority()获得优先级,setPriority(int)设置线程优先级,getStatus()获取线程状态,isInterupted()判断是否被打断,isAlive()判断线程是否存活,interrupt()打断线程,interrupted()判断当前线程是否被打断。
- currentThread()获取当前正在执行的线程,sleep(long n)让当前执行的线程休眠n毫秒,休眠时让出其cpu的时间片给其它线程。
- yield()提示线程调度器让出当前线程对CPU的使用。
3.7.2常见方法start vs run
run:称为线程体,包含了要执行的这个线程的内容,方法运行结束,此线程随即终止。直接调用 run 是在主线程中执行了 run,没有启动新的线程,需要顺序执行
start:使用 start 是启动新的线程,此线程处于就绪(可运行)状态,通过新的线程间接执行 run 中的代码

说明:线程控制资源类
run() 方法中的异常不能抛出,只能 try/catch
- 因为父类中没有抛出任何异常,子类不能比父类抛出更多的异常
- 异常不能跨线程传播回 main() 中,因此必须在本地进行处理
3.7.3sleep 与 yield
sleep:
- 调用 sleep 会让当前线程从
Running进入Timed Waiting状态(阻塞) - sleep() 方法的过程中,线程不会释放对象锁
- 其它线程可以使用 interrupt 方法打断正在睡眠的线程,这时 sleep 方法会抛出 InterruptedException
- 睡眠结束后的线程未必会立刻得到执行,需要抢占 CPU
- 建议用 TimeUnit 的 sleep 代替 Thread 的 sleep 来获得更好的可读性
1.打断sleep的示例
程序思路,t1.start执行完,输出begin,然后休眠,执行t1的run方法输出enter slee…,然后休眠,1秒到后输出interrupt,最终t1.interrupt方法被调用,休眠线程立刻被打断,开始执行wake up….
1 | @Slf4j(topic="c.Test7") |
2.建议用TimeUnit的sleep代替Thread的sleep来获得更好的可读性。
1 | @Slf4j(topic = "c.Test8") |
yield:
- 某个线程调用yield,可以让出CPU的使用权。
- 调用yield会让当前线程从Running进入Runnable就绪状态,然后调度执行其它线程。
- 具体的实现依赖于操作系统的任务调度器
- 会放弃 CPU 资源,锁资源不会释放
3.7.4线程优先级

- 线程优先级会提示(hint)调度器优先调度该线程,但它仅仅只是一个提示,调度器可以忽略它。
- 如果cpu较忙,优先级高的线程会获得更多的时间片,但cpu如果闲时,优先级几乎没作用。
1 | @Slf4j(topic="c.Test4") |
3.7.5sleep的应用
在没有利用cpu来计算时,不要让while(true)空转浪费cpu,这时可以使用yield或sleep来让出cpu的使用权给其它程序。

可以用wait或者条件变量达到类似的效果。但需要加锁,并且需要设置相应的唤醒操作,一般适用于要进行同步的场景。sleep适合无锁同步的场景。
只写while(true)
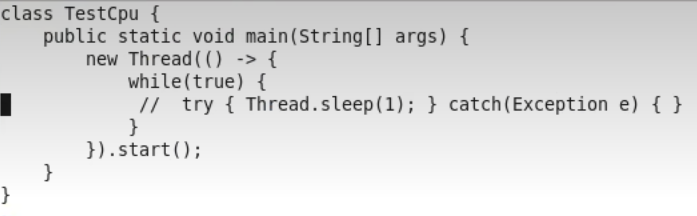
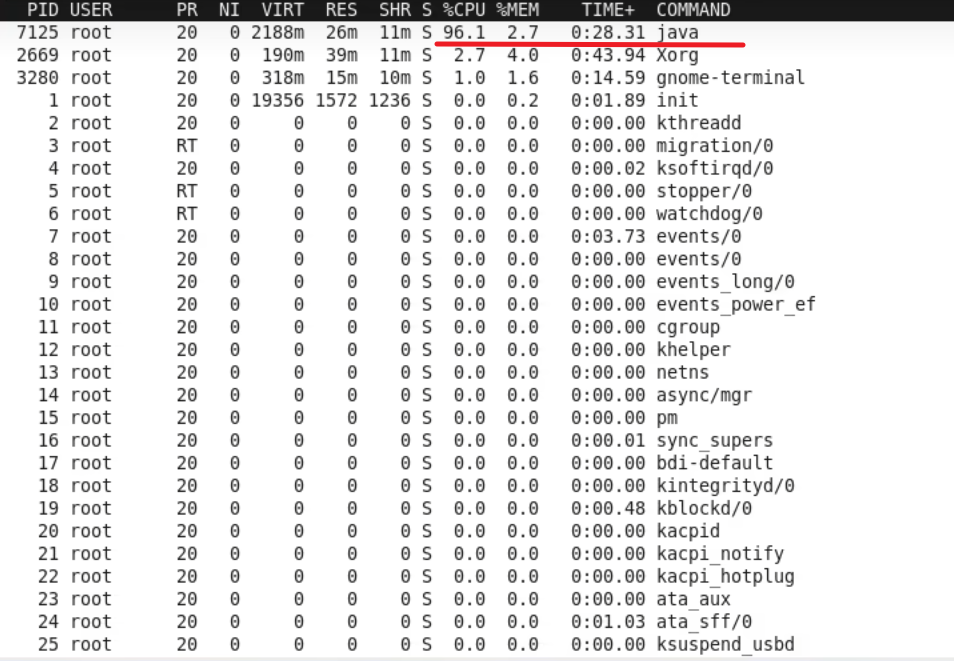
占用率非常高
当把注释去掉后(加了sleep):

只占用了3%左右
3.7.6join方法详解
public final void join():等待这个线程结束
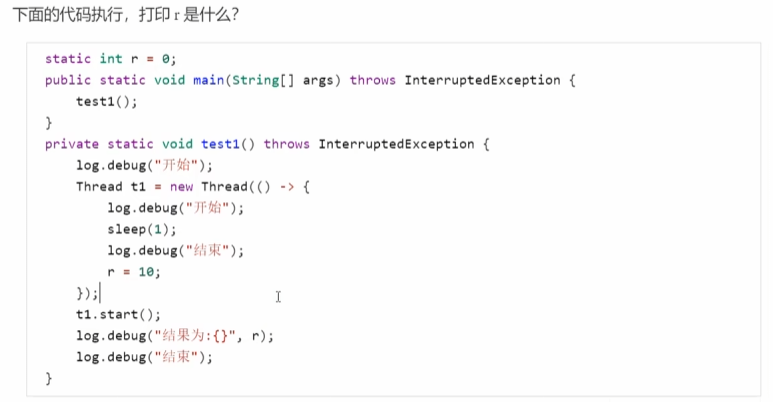

此时若想让r=10,则需要在t1.start()的下面加上t1.join()表示等待t1执行结束返回结果,主线程再执行。
1 | @Slf4j(topic="c.Test5") |
原理:调用者轮询检查线程 alive 状态,t1.join() 等价于:
1 | public final synchronized void join(long millis) throws InterruptedException { |
- join 方法是被 synchronized 修饰的,本质上是一个对象锁,其内部的 wait 方法调用也是释放锁的,但是释放的是当前的线程对象锁,而不是外面的锁
- 当调用某个线程(t1)的 join 方法后,该线程(t1)抢占到 CPU 资源,就不再释放,直到线程执行完毕
join同步应用
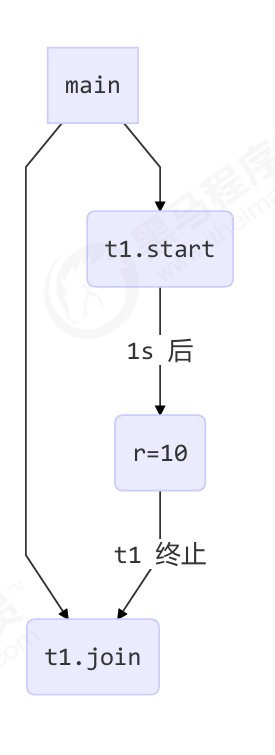
如果主线程不止等一个线程的运行结果,要等多个线程运行结果该怎么做呢
很简单那就是调用不同线程的join方法
问,下面代码 cost 大约多少秒?
1 | @Slf4j(topic = "c.TestJoin") |
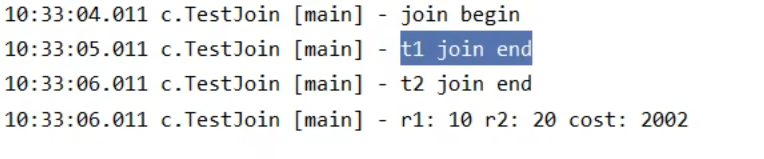
分析如下 看左图
- 第一个 join:等待 t1 时, t2 并没有停止, 而在运行
- 第二个 join:1s 后, 执行到此, t2 也运行了 1s, 因此也只需再等待 1s
如图打印2002毫秒即2s
如果颠倒两个join?先t2.join后t1.join(还是2s)看右图
join限时同步(有时效的等待)
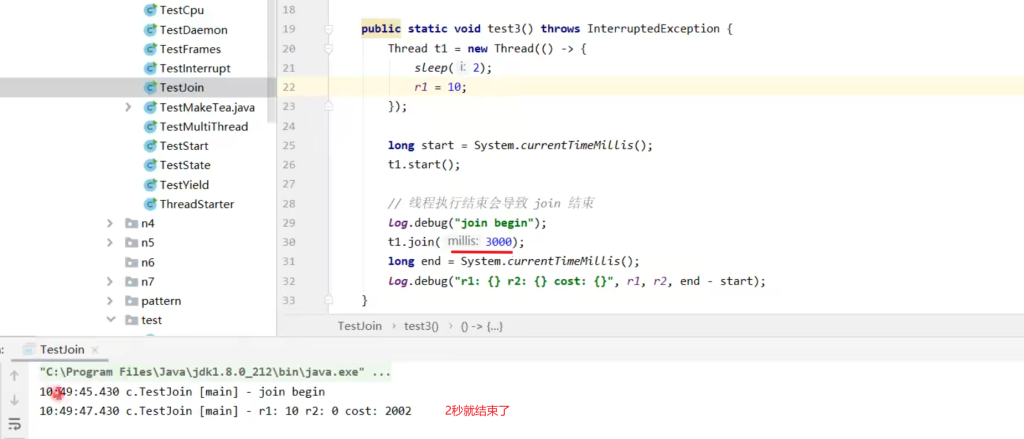
下面给t1.join()设置了1500毫秒等待时间,因为小于线程睡眠时间,所以没法能线程苏醒改变r,输出结果为r1=0。
1 | @Slf4j(topic = "c.TestJoin") |
当把等待时间设为3秒时,线程提前结束了,join也会提前结束
3.7.7interrupt方法详解
打断线程
public void interrupt():打断这个线程,异常处理机制public static boolean interrupted():判断当前线程是否被打断,打断返回 true,清除打断标记,连续调用两次一定返回 falsepublic boolean isInterrupted():判断当前线程是否被打断,不清除打断标记
打断的线程会发生上下文切换,操作系统会保存线程信息,抢占到 CPU 后会从中断的地方接着运行(打断不是停止)
打断 sleep,wait,join 的线程(打断阻塞)
这几个方法都会让线程进入阻塞状态
打断 sleep 的线程, 会清空打断状态,以 sleep 为例
1 | @Slf4j(topic="c.Test6") |
如果线程是在睡眠中被打断会以报错的形式出现,打断标记为false
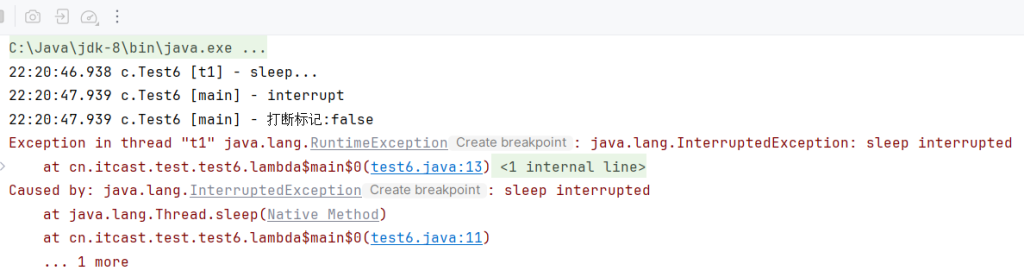
打断正常运行的线程
打断正常运行的线程, 不会清空打断状态
如果在main方法中调用t1的interrupt方法,t1线程只是会被告知有线程想打断,不会强制被退出。此时isinterrupted状态会被设为true,此时可以利用该状态来让线程决定是否退出。
1 | @Slf4j(topic="c.Test7") |

补充两阶段终止模式 -interrupt
在一个线程T1中如何优雅的终止线程T2,这里的优雅指的是给T2一个料理后事的机会。
错误思路:
1.使用线程对象的stop方法停止线程。stop方法会真正杀死线程,如果线程锁住了共享资源,那么当它被杀死后就再也没有机会释放锁,其它线程将永远无法获取锁。
2.使用System.exit(int)方法会直接把方法停止,直接把进程停止。
思路模式:
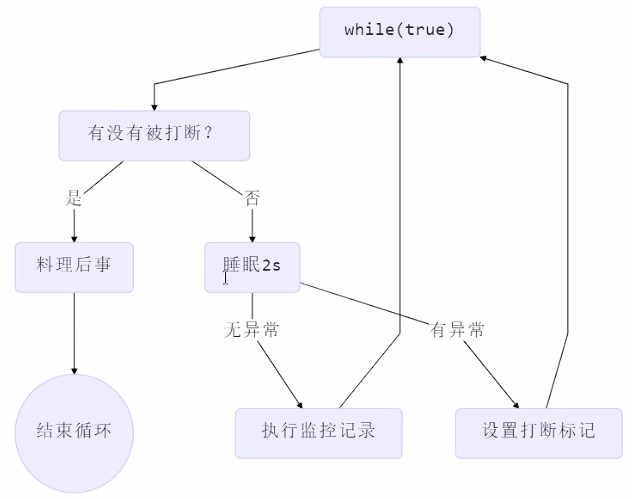
在工作中被打断,打断标记是true,会进入到料理后事。
在睡眠是被打断,会抛出异常,此时打断标记是false,此时可以重新设置打断标记为true。
设计模式两阶段终止interrupt实现:
1 | (topic = "c.TwoPhaseTermination") |
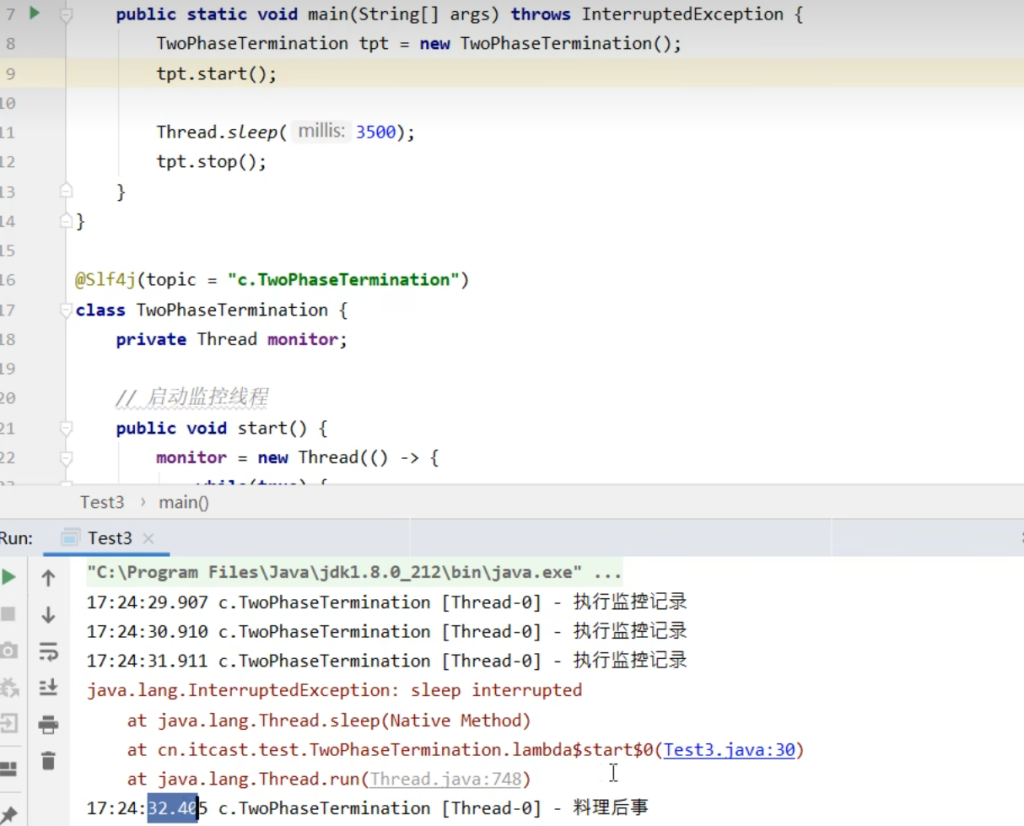
细节:
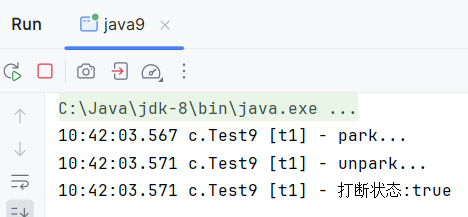
interrupt打断park
1 | @Slf4j(topic="c.Test9") |
3.7.8过时方法
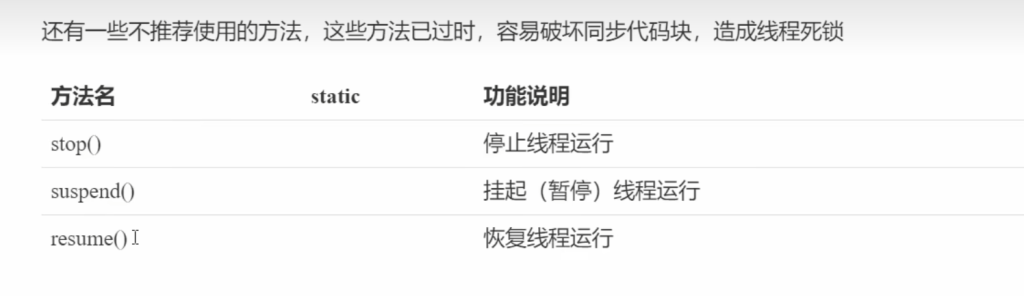
不推荐使用的方法,这些方法已过时,容易破坏同步代码块,造成线程死锁:
public final void stop():停止线程运行废弃原因:方法粗暴,除非可能执行 finally 代码块以及释放 synchronized 外,线程将直接被终止,如果线程持有 JUC 的互斥锁可能导致锁来不及释放,造成其他线程永远等待的局面public final void suspend():挂起(暂停)线程运行废弃原因:如果目标线程在暂停时对系统资源持有锁,则在目标线程恢复之前没有线程可以访问该资源,如果恢复目标线程的线程在调用 resume 之前会尝试访问此共享资源,则会导致死锁public final void resume():恢复线程运行
3.7.9守护线程
默认情况下,Java进程需要等待所有的线程都运行结束,才会结束。
有一种特殊的线程叫守护线程,只要其它非守护线程执行结束了,即时守护线程的代码没有执行完,也会强制结束。
在t1启动前调用setDaemon方法开启守护线程,如果主线程运行结束,守护线程也会结束
1 | @Slf4j(topic="c.Test15") |
注意
- 垃圾回收器线程就是一种守护线程,如果程序停止,垃圾回收线程也会被强制停止。
- Tomcat 中的 Acceptor 和 Poller 线程都是守护线程,所以 Tomcat 接收到 shutdown 命令后,不会等待它们处理完当前请求
3.8线程状态
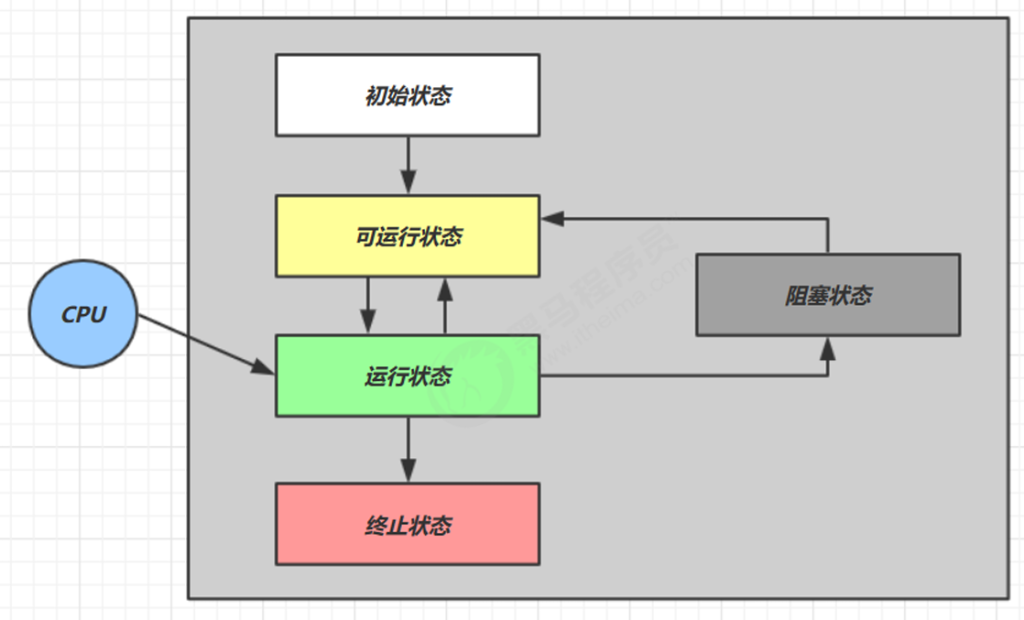
3.8.1五种( 操作系统 层面)
这是从 操作系统 层面来描述的

3.8.2线程状态六种(Java API 层面)
这是从 Java API 层面来描述的
根据 Thread.State 枚举,分为六种状态
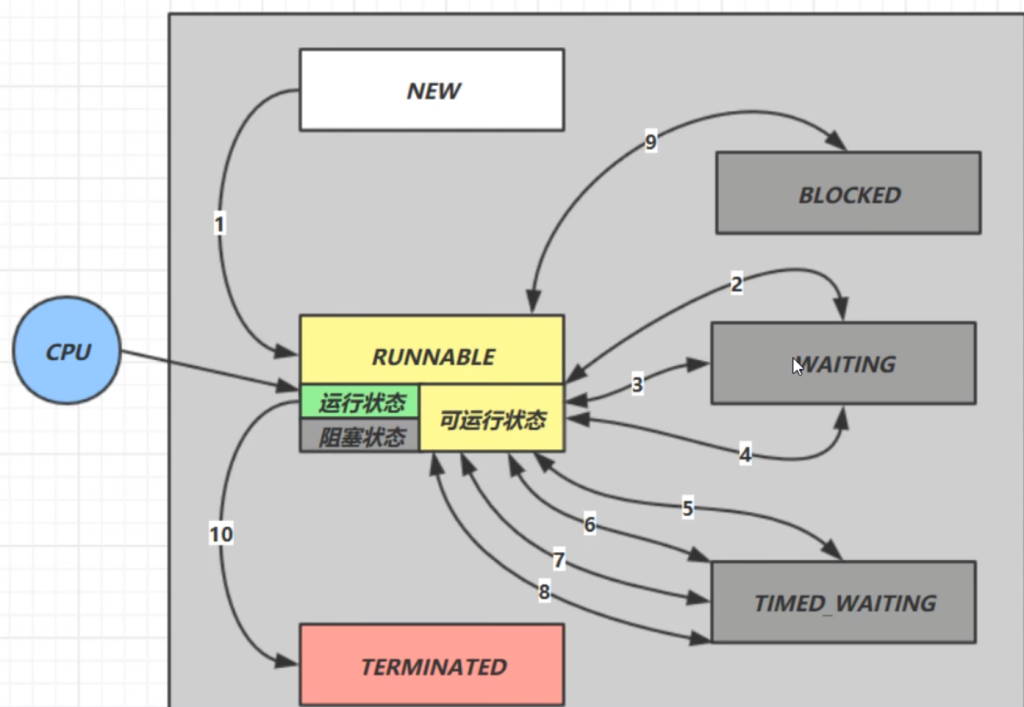
| 线程状态 | 导致状态发生条件 |
|---|---|
| NEW(新建) | 线程刚被创建,但是并未启动,还没调用 start 方法,只有线程对象,没有线程特征 |
| Runnable(可运行) | 线程可以在 Java 虚拟机中运行的状态,可能正在运行自己代码,也可能没有,这取决于操作系统处理器,调用了 t.start() 方法:就绪(经典叫法) |
| Blocked(阻塞) | 当一个线程试图获取一个对象锁,而该对象锁被其他的线程持有,则该线程进入 Blocked 状态;当该线程持有锁时,该线程将变成 Runnable 状态 |
| Waiting(无限等待) | 一个线程在等待另一个线程执行一个(唤醒)动作时,该线程进入 Waiting 状态,进入这个状态后不能自动唤醒,必须等待另一个线程调用 notify 或者 notifyAll 方法才能唤醒 |
| Timed Waiting (限期等待) | 有几个方法有超时参数,调用将进入 Timed Waiting 状态,这一状态将一直保持到超时期满或者接收到唤醒通知。带有超时参数的常用方法有 Thread.sleep 、Object.wait |
| Teminated(结束) | run 方法正常退出而死亡,或者因为没有捕获的异常终止了 run 方法而死亡 |
- NEW → RUNNABLE:当调用 t.start() 方法时,由 NEW → RUNNABLE
- RUNNABLE <—> WAITING:
- 调用 obj.wait() 方法时调用 obj.notify()、obj.notifyAll()、t.interrupt():
- 竞争锁成功,t 线程从 WAITING → RUNNABLE
- 竞争锁失败,t 线程从 WAITING → BLOCKED
- 当前线程调用 t.join() 方法,注意是当前线程在 t 线程对象的监视器上等待
- 当前线程调用 LockSupport.park() 方法
- 调用 obj.wait() 方法时调用 obj.notify()、obj.notifyAll()、t.interrupt():
- RUNNABLE <—> TIMED_WAITING:调用 obj.wait(long n) 方法、当前线程调用 t.join(long n) 方法、当前线程调用 Thread.sleep(long n)
- RUNNABLE <—> BLOCKED:t 线程用 synchronized(obj) 获取了对象锁时竞争失败
3.9习题
-应用之统筹分析
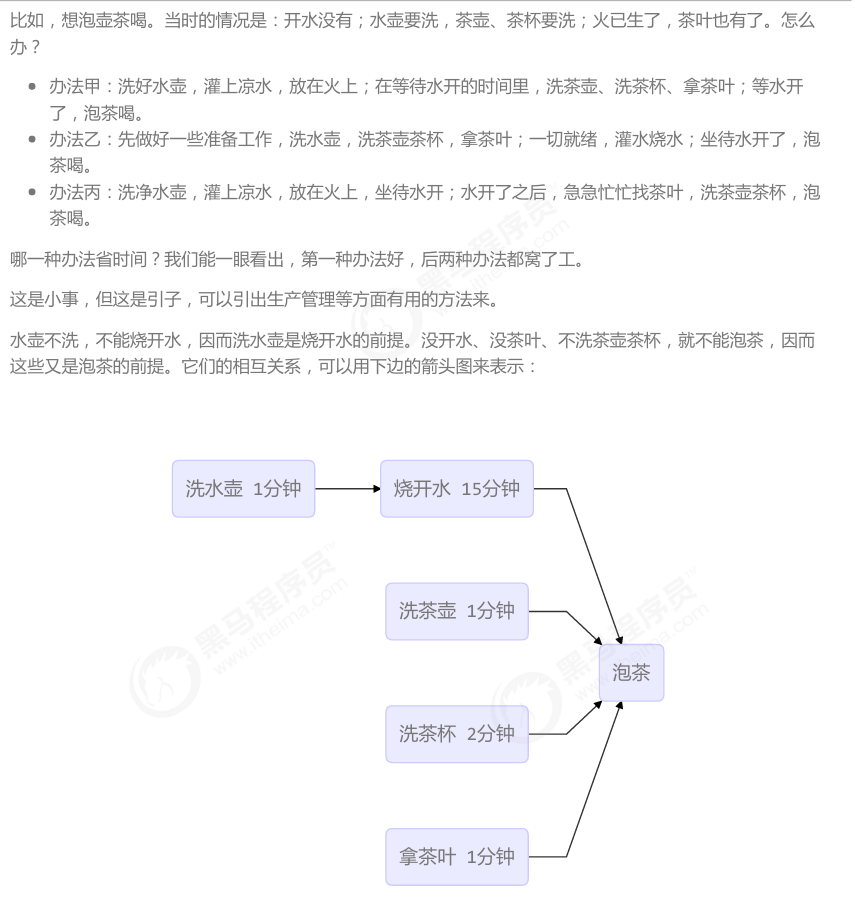
多线程找到最优的方法:

-应用之统筹实现
1 | @Slf4j(topic = "c.Test16") |
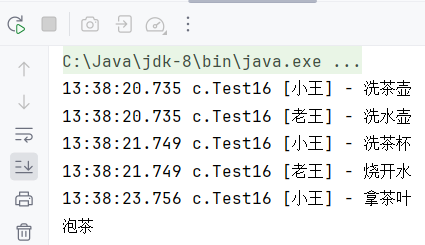
缺点:上面模拟的是小王等老王的水烧开了,小王泡茶,如果反过来要实现老王等小王的茶叶拿过来,老王泡茶呢?代码最好能适应2种情况。
上面的两个线程各执行各的,如果要模拟老王把水壶交给小王泡茶,或模拟小王把茶叶交给老王泡茶呢?
其他的解法我们后续再说

3.10小结

4.共享模型之管程
本章内容
- 共享问题
- synchronized
- 线程安全分析
- Monitor
- wait/notify
- 线程状态转换
- 活跃性
- Lock
4.1共享带来的问题(上下文切换)
多线程下访问共享资源,因为分时系统导致的数据不一致等安全问题
java中的体现
1 | @Slf4j(topic="c.Test12") |
i++和i—编译成字节码不是一条代码:执行时需要时间,在这段时间内还未执行完时可能就因为上下文切换导致指令交错。

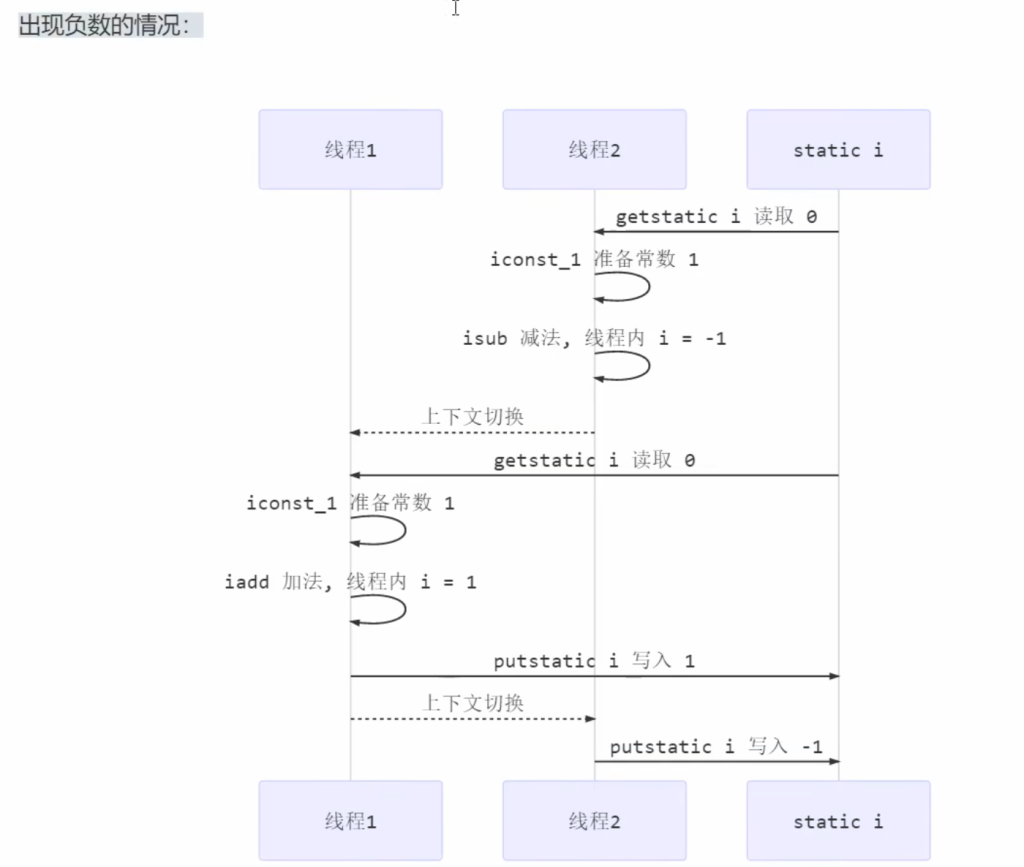
造成数据不一致的原因是:
某个线程的事情还没干完,数据还没来得及写入,上下文就切换了。根本原因:上下文切换导致指令交错。
临界区与竞态条件
临界区:

临界资源:一次仅允许一个进程使用的资源成为临界资源
临界区:访问临界资源的代码块
竞态条件:多个线程在临界区内执行,由于代码的执行序列不同而导致结果无法预测,称之为发生了竞态条件
一个程序运行多个线程是没有问题,多个线程读共享资源也没有问题,在多个线程对共享资源读写操作时发生指令交错,就会出现问题
4.2synchronized解决方案(同步块)
为了避免临界区的竞态条件发生(解决线程安全问题):
- 阻塞式的解决方案:synchronized,lock
- 非阻塞式的解决方案:原子变量
管程(monitor):由局部于自己的若干公共变量和所有访问这些公共变量的过程所组成的软件模块,保证同一时刻只有一个进程在管程内活动,即管程内定义的操作在同一时刻只被一个进程调用(由编译器实现)
synchronized:对象锁,保证了临界区内代码的原子性,采用互斥的方式让同一时刻至多只有一个线程能持有对象锁,其它线程获取这个对象锁时会阻塞,保证拥有锁的线程可以安全的执行临界区内的代码,不用担心线程上下文切换
互斥和同步都可以采用 synchronized 关键字来完成,区别:
- 互斥是保证临界区的竞态条件发生,同一时刻只能有一个线程执行临界区代码
- 同步是由于线程执行的先后、顺序不同、需要一个线程等待其它线程运行到某个点
性能:
- 线程安全,性能差
- 线程不安全性能好,假如开发中不会存在多线程安全问题,建议使用线程不安全的设计类
synchronized
语法
1 | synchronized(对象){ |
解决:
1 | @Slf4j(topic="c.Test12") |
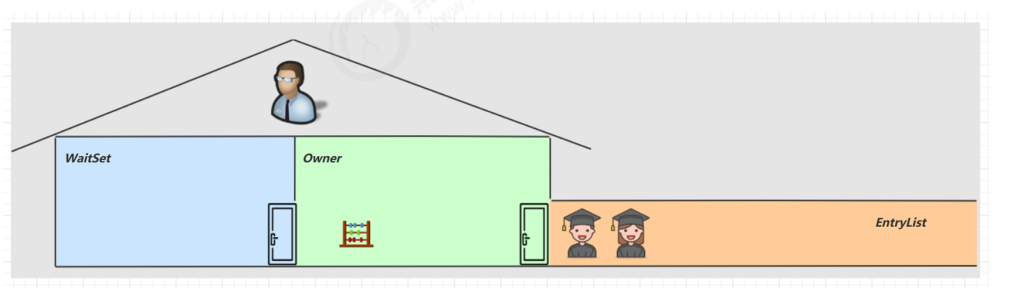
synchronized的理解
假如t1通过synchronized拿到锁以后,但是时间片不幸用完了,但这个锁仍旧是t1的,只有时间片下次重新轮到t1时才能继续执行。
只有当t1执行完synchronized()块内的代码,会释放锁。其它线程才能竞争。

用图来理解:
当锁被占用时,就算指令没执行完上下文切换,其它线程也获取不到锁,只有当拥有锁的线程的所有代码执行完才能释放锁。
思考

1.把加锁提到for循环外,相当于5000次for循环都视为一个原子操作。
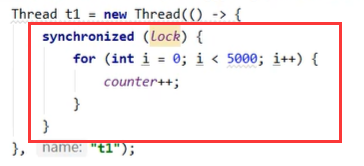
2.锁的不是一个对象,注意要保护共享资源必须要多个线程锁同一个对象
3.如果线程1加锁,线程2没加锁会导致的情况:线程2去访问临界资源时,不会尝试获取对象锁,因此不会被阻塞住,仍然能继续访问。
面向对象代码改进
1 | @Slf4j(topic="c.Test12") |
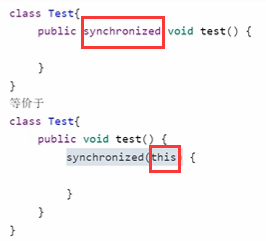
4.3方法上的 synchronized(同步方法)
synchronized可以加在方法上,相当于锁住方法。
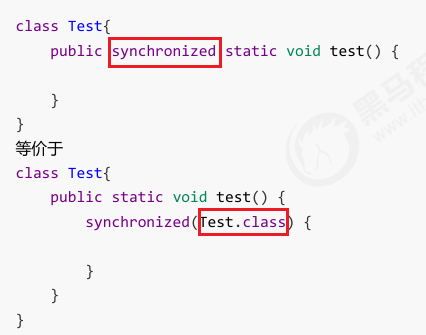
synchronized加在静态方法上,相当于所住类。
4.4线程八锁
线程八锁就是考察 synchronized 锁住的是哪个对象
说明:主要关注锁住的对象是不是同一个
- 锁住类对象,所有类的实例的方法都是安全的,类的所有实例都相当于同一把锁
- 锁住 this 对象,只有在当前实例对象的线程内是安全的,如果有多个实例就不安全

4.5变量的线程安全分析
这部分可参考JVM(原理篇)逃逸分析部分

成员变量与静态变量是否线程安全?
| 是否共享 | 状态是否可变 | 线程安全性 |
|---|---|---|
| 没有共享 | 不可变/可变均可 | ✔ 安全 |
| 有共享 | 只读 | ✔ 安全 |
| 有共享 | 有读写 | ❌ 不安全,必须加锁(临界区) |
局部变量是否线程安全?
| 情况 | 是否线程安全 |
|---|---|
| 局部变量本身是基本类型或不可变对象 | ✔ 安全(每个线程独立栈帧) |
| 局部变量是引用对象,且未“逃逸” | ✔ 安全 |
| 局部变量是引用对象,逃出了作用域(如被线程持有) | ❌ 不安全,需同步控制 |
局部变量线程安全分析
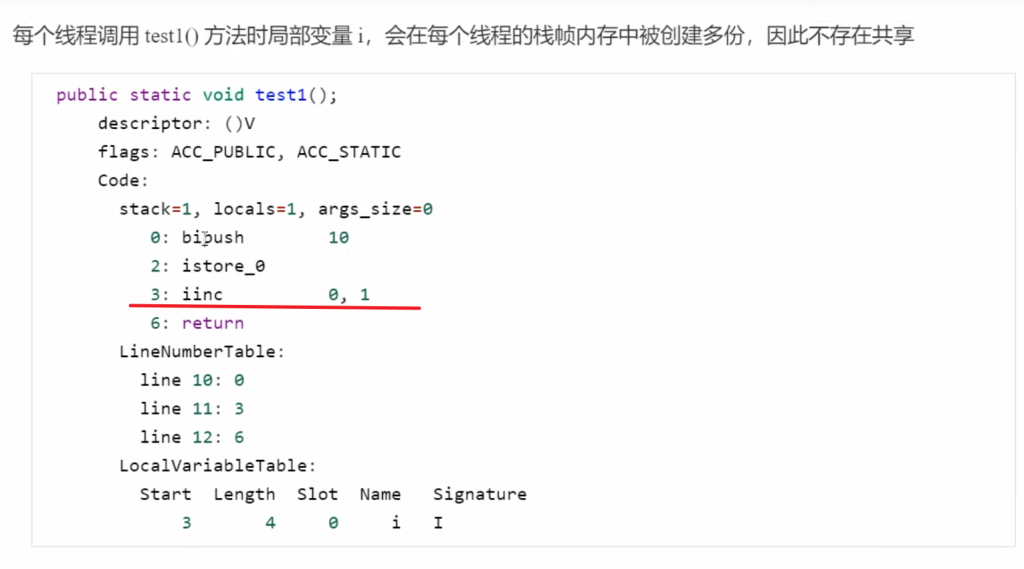
1 | public static void test1() { |
每个线程执行 test1() 都会在自己的栈中创建变量 i,互不影响,所以安全。
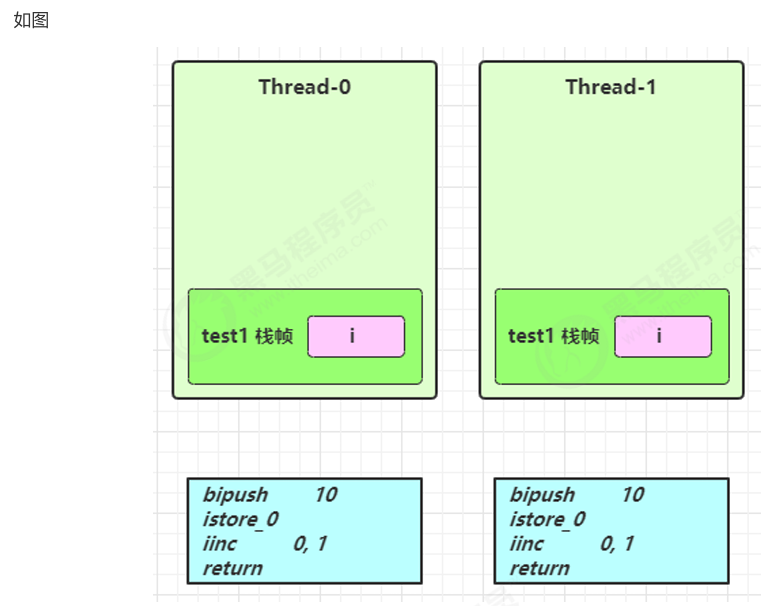
局部变量引用线程安全分析
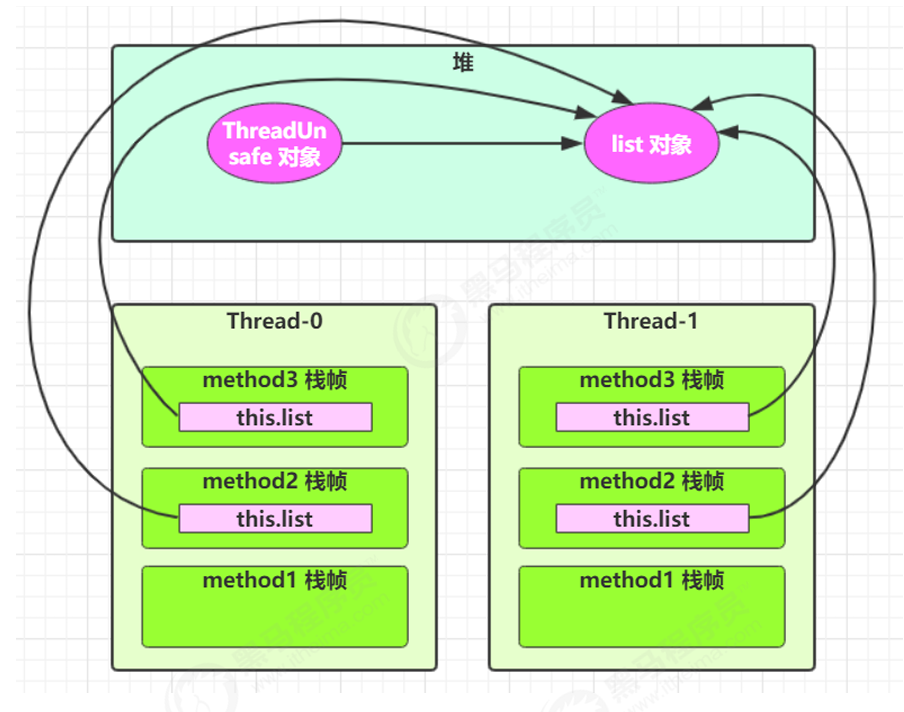
创建2个线程,然后每个线程去调用method1:
1 | class ThreadUnsafe { |
其中一种情况是,如果线程2 还未 add,线程1 remove 就会报错:
1 | Exception in thread "Thread1" java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException: Index: 0, Size: 0 |
- 多个线程共享
list成员变量 - 当线程1还未
add,线程2就remove,就会抛出IndexOutOfBoundsException - 原因是
list的读写操作未加锁
分析:
无论哪个线程中的 method2 引用的都是同一个对象中的 list 成员变量
method3 与 method2 分析相同
使用局部变量消除线程安全问题
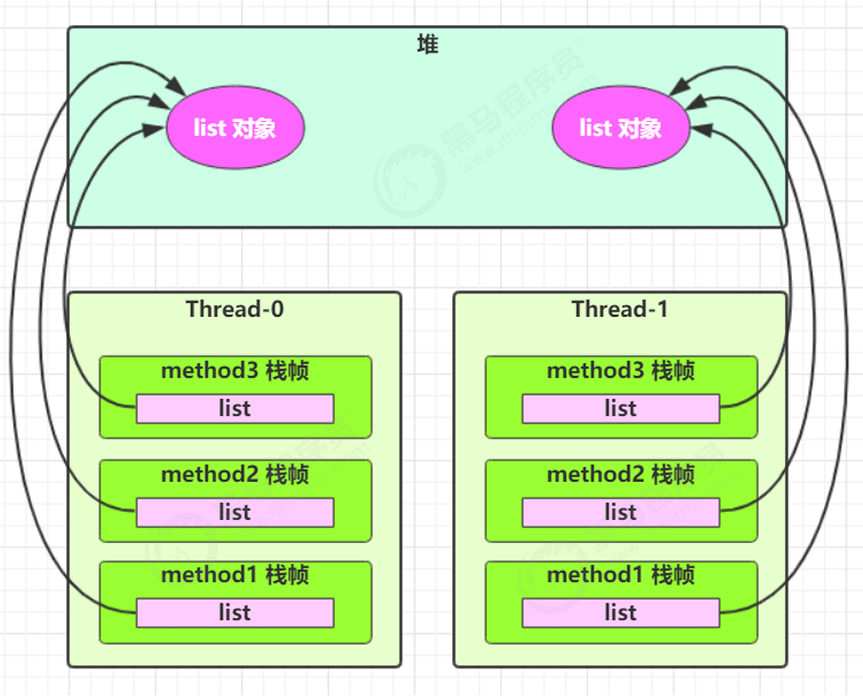
将list改为局部变量后,放到方法内:
1 | class ThreadSafe { |
- 分析:
- 每次调用
method1都会创建新的list,没有共享,线程安全。 method2和method3只是使用该局部变量引用,不涉及跨线程共享。
局部变量暴露引用线程安全分析 (方法修饰符带来的线程安全隐患)
方法访问修饰符带来的思考,如果把 method2 和 method3 的方法修改为 public 会不会代理线程安全问题?
若将 method2 / method3 改为 public,可能被外部线程调用,引发线程安全问题。
1 | class ThreadSafeSubClass extends ThreadSafe { |
private和final有助于保证线程安全- 避免方法被子类覆盖或外部调用是控制对象封装行为的基础
- 属于“开闭原则”中“闭”的一部分:对修改关闭
常见线程安全类
以下类的单个方法是线程安全的,也就是说多个线程同时调用它们的同一个实例的方法,不会发生数据冲突。
| 类名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
String |
不可变类,线程安全 |
Integer |
同上,不可变类 |
StringBuffer |
线程安全的字符串容器(内部使用 synchronized) |
Random |
线程安全版本为 ThreadLocalRandom(注意早期版本并不线程安全) |
Vector |
线程安全的 List |
Hashtable |
线程安全的 Map |
java.util.concurrent 包 |
含有大量现代高性能线程安全类,如 ConcurrentHashMap、CopyOnWriteArrayList 等 |
这里说它们是线程安全的是指,多个线程调用它们同一个实例的某个方法时,不会造成数据不一致,是线程安全的。比如:
1 | Hashtable table = new Hashtable(); |
- 这样的使用是线程安全的,因为
put()是原子操作。 - 它们的每个方法是原子的
- 但注意它们多个方法的组合不是原子的,见后面分析
线程安全类方法的组合(线程安全类 ≠ 线程安全程序)
不可变类线程安全性
像 String、Integer 这些不可变类,为什么是线程安全的?
因为对象一旦创建,状态无法更改,所以不存在“状态修改的竞态条件”。
有同学或许有疑问,String 有 replace,substring 等方法【可以】改变值啊,那么这些方法又是如何保证线程安全的呢?
例子:简单不可变类
1 | public class Immutable{ |
- 每次调用
add()并不改变原对象,而是返回一个新的对象。 - 多线程中同时操作
Immutable实例,不会互相影响,自然线程安全。
回答常见疑问:
String.replace()/substring()看起来在“修改”值,它们安全吗?
它们是线程安全的,因为这些方法不会修改原对象,而是返回新对象,String 本身始终不可变。
总结:
| 类类型 | 是否线程安全 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
不可变类(如 String、Integer) |
✔ | 因为不可变,不存在写操作 |
Synchronized 类(如 Vector、Hashtable) |
✔(单个方法) | 多方法组合需手动加锁 |
JUC 并发容器(如 ConcurrentHashMap) |
✔(更细粒度) | 推荐用于高并发场景 |
| 方法组合调用 | ❌ | 不具备原子性,需额外同步 |
实例分析
实例1:Servlet 中成员变量的线程安全性
1 | public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet { |
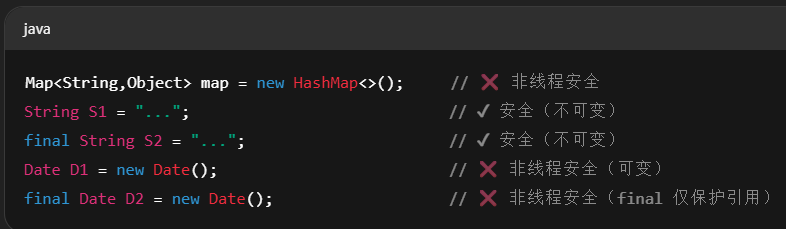
- 可变对象 + 被共享 ➜ 非线程安全
- 不可变对象(如
String)是线程安全的 final只能保护引用地址不变,无法保证引用对象的状态不可变(如Date)
实例2:成员变量写操作(count++)导致线程不安全
下面这段非线程安全:
1 | public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet { |
问题: count++ 实际包含读 -> 改 -> 写,存在线程间交叉执行,造成数据丢失
实例3:AOP 切面中成员变量共享,线程不安全
下面这段非线程安全:
1 |
|
说明:
Spring 中默认组件是单例的,成员变量 start 被所有线程共享 ➜ 线程不安全
实例4:局部变量无共享 ➜ 线程安全
下面这个方法是线程安全,因为没有成员变量,也就是类下没有定义变量。变量在方法内部,各自都在线程的栈内存中,因此是线程安全的。
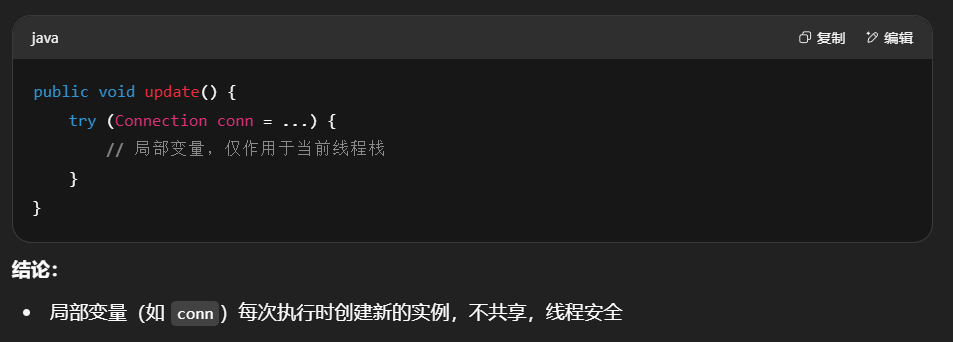
1 | public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet { |
实例5:类中只有可变的成员变量(如 conn) ➜ 仍然不安全
1 | private Connection conn = null; |
问题:
- 多个线程操作同一个
conn,存在共享 ➜ 非线程安全
实例6:对象内部通过 new 创建依赖类 ➜ 安全(不共享)
1 | public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { |
分析:
- 每个线程调用时都 new 了不同对象 ➜ 没有共享 ➜ 安全
实例7:“外星方法”带来线程不安全
1 | public void bar() { |
概念:“外星方法”
- 将可变对象传给外部不可控方法,可能在其他线程中被并发使用,破坏封装性
实例8:锁定 Integer 无效
private static Integer i = 0;
1 | synchronized (i) { |
结论:
Integer是不可变类,i++实际是重新赋值新对象- 所以
synchronized(i)每次锁的是不同对象 ➜ 锁失效 ➜ 非线程安全
最终总结:线程安全分析思维模型
| 场景 | 线程是否安全 | 原因或说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 局部变量(基本类型或引用对象未逃逸) | ✔ 安全 | 不共享,每个线程独立栈帧 |
| 成员变量(可变 & 被共享) | ❌ 不安全 | 需要加锁或变为局部变量 |
| 不可变类(如 String、Integer) | ✔ 安全 | 状态不可变,天然线程安全 |
| 方法中 new 出来的对象 | ✔ 安全 | 不共享,线程私有 |
| 对象作为参数传给未知外部方法(外星方法) | ❌ 风险高 | 可能被异步线程引用 |
| 使用 synchronized 锁住易变对象引用(如 Integer) | ❌ 锁无效 | 对象地址变,锁失效 |
| 单例类中共享成员变量 | ❌ 不安全 | 默认是所有线程共享一份对象 |
4.6习题
习题- 卖票
测试下面代码是否存在线程安全问题,并尝试改正
证明方法:余票数和卖出去的票数相等,代表前后一致,没有线程安全问题。
1 | @Slf4j(topic="c.ExerciseSell") |
- 将sell方法声明为synchronized即可
- 注意只将对count进行修改的一行代码用synchronized括起来也不行。对count大小的判断也必须是为原子操作的一部分,否则也会导致count值异常。
另外,用下面的代码行不行,为什么?
1 | List<Integer> sellCount = new ArrayList<>(); |
- 不行,因为sellCount会被多个线程共享,必须使用线程安全的实现类。
习题 -转账
这道题的难点在于有2个共享变量,一个是a的账户中的money,一个是b的账户中的money。
1 | @Slf4j(topic="c.ExerciseTransfer") |
加入:synchronized(Account.class),相当于锁住两个账户的临界资源,缺点是n个账户只能有2个账户进行交互。后续会再次优化这个方法
4.7 Monitor 概念
Java 中的每一个对象在内存布局中通常分为三部分:详细见JVM原理篇2、对象在堆上是如何存储的?
| 部分 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 对象头(Object Header) | 包含对象的运行时元信息,如锁状态、GC信息、类元信息等 |
| 实例数据(Instance Data) | 包含类中定义的变量 |
| 对齐填充(Padding) | 用于保证对象大小是 8 字节的整数倍,提升性能 |
JAVA对象头
Klass word是一个指针,指向某个对象从属的Class,找到类对象,每个对象通过Klass来辨明自己的类型。
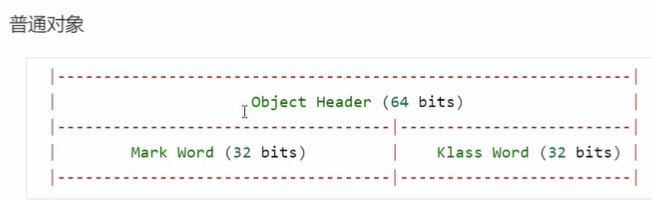
普通对象头(64 bits)
| 内容 | 大小 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Mark Word | 32 bits | 存储锁信息、GC标志等 |
| Klass Word | 32 bits | 指向 class 元数据的指针,确定对象类型 |
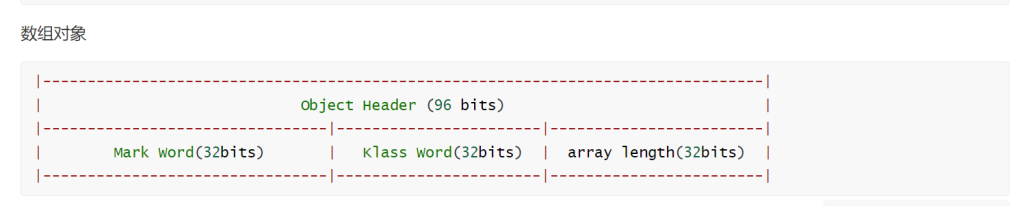
| 区域 | 位数 | 内容 |
|---|---|---|
| Mark Word | 32 bits | 同上 |
| Klass Pointer | 32 bits | 同上 |
| 数组长度 | 32 bits | 数组长度信息 |

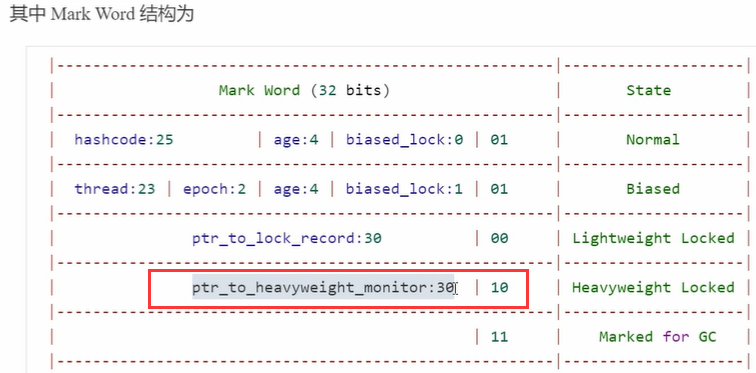
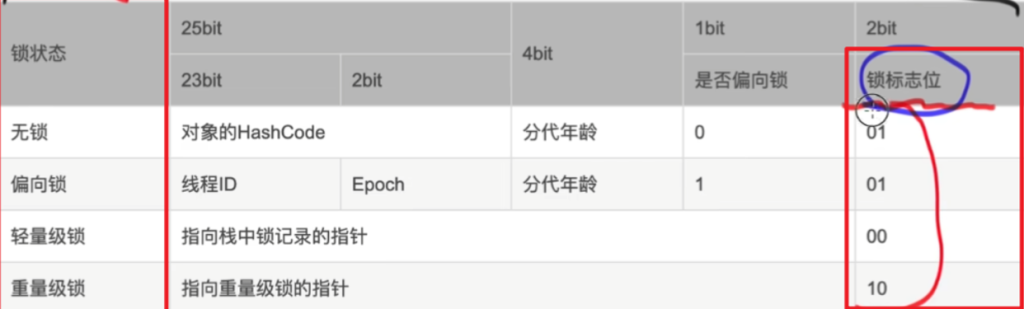
Mark Word 的锁状态详解(32位)
Mark Word 是 Java 对象头的核心,存储了锁信息。根据锁的状态,它的结构会发生变化。
| 状态 | Mark Word 中的结构(32位) |
|---|---|
| 无锁(Normal) | hashcode:25 |
| 偏向锁(Biased) | thread:23 |
| 轻量级锁 | ptr_to_lock_record:30 |
| 重量级锁 | ptr_to_heavyweight_monitor:30 |
| GC 标记 | —— |
附上各种锁:
| 锁状态 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 无锁 | 普通状态,未被任何线程持有锁 |
| 偏向锁 | 偏向某个线程,能提高无竞争场景的性能 |
| 轻量级锁 | 多线程竞争时升级为轻量级锁,使用自旋等待 |
| 重量级锁 | 自旋失败后升级为重量级锁,阻塞其他线程 |
| GC标记 | 用于垃圾回收阶段标记对象 |
扩展:64 位虚拟机下 Mark Word 的结构更长
| 状态 | Mark Word(64位)部分结构 |
|---|---|
| 无锁 | unused:25 |
| 偏向锁 | thread:54 |
| 轻量级锁 | ptr_to_lock_record:62 |
| 重量级锁 | ptr_to_heavyweight_monitor:62 |
Monitor 工作原理
什么是 Monitor?
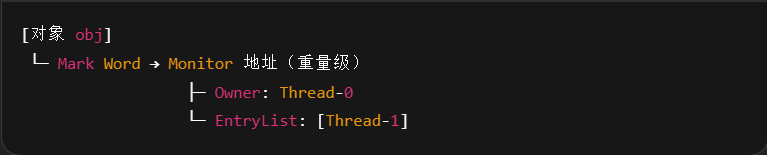
Monitor 被翻译为 监视器 或 管程,是 JVM 实现 synchronized 的核心机制。
✅ 每一个 Java 对象都可以和一个 Monitor 关联
✅ 使用synchronized(obj)时,该对象的 Mark Word 会指向对应的 Monitor
obj是java的对象,Monitor是操作系统提供的监视器,调用synchronized是将obj和Monitor进行关联,相当于在MarkWord里面记录Monitor里面的指针地址。
Monitor 结构如下:
Monitor 本质上是操作系统级的同步原语,它主要包括:
| 组件名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| Owner | 当前持有锁的线程 |
| EntryList | 其他试图进入锁但被阻塞的线程队列 |
| WaitSet | 已获得锁但执行 wait() 而进入等待状态的线程 |
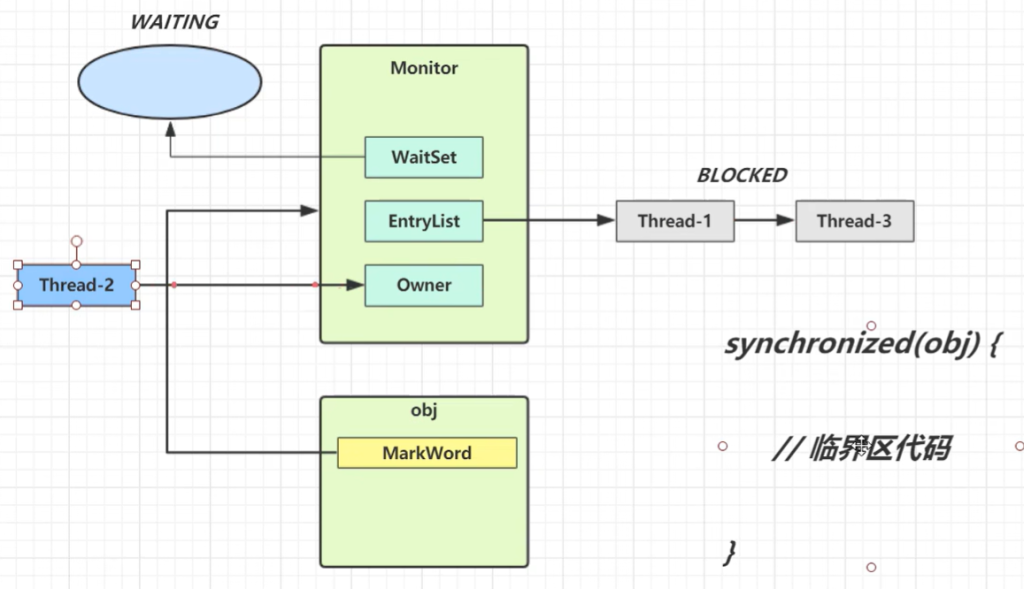
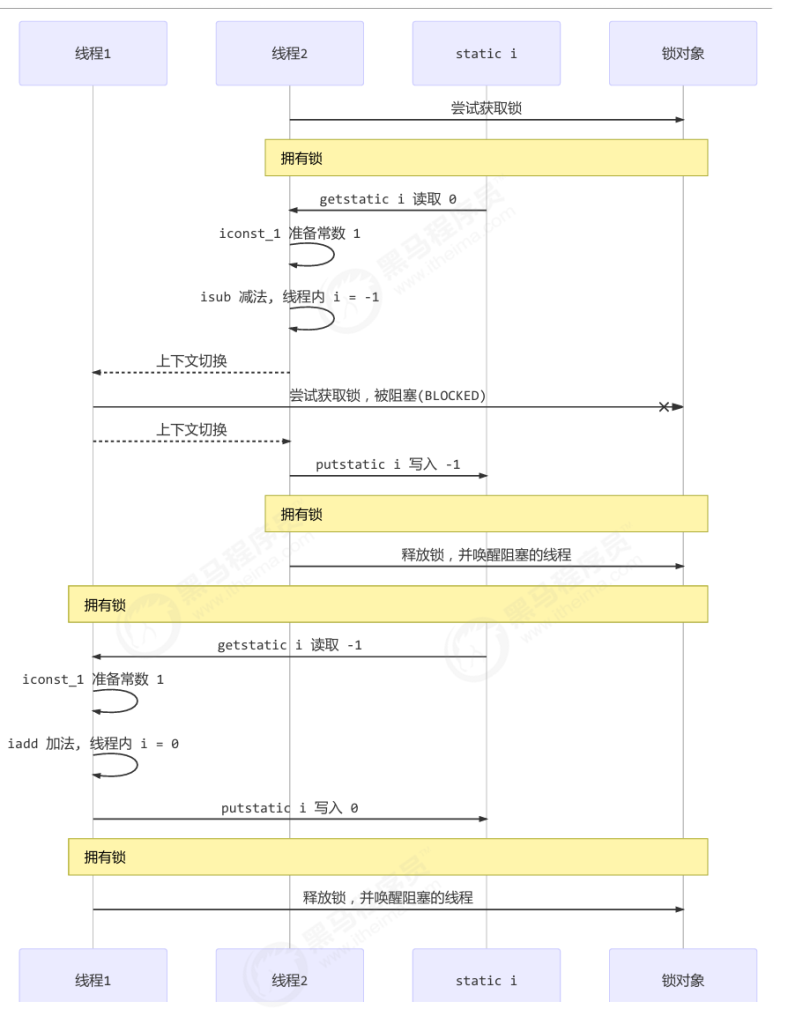
Monitor里面的Owner记录的是当前哪个线程享有这个资源,EntryList是一个线程队列,来一个线程就进入到阻塞队列。
- 刚开始 Monitor 中 Owner 为 null
- 当 Thread-2 执行 synchronized(obj) 就会将 Monitor 的所有者 Owner 置为 Thread-2,Monitor中只能有一 个 Owner
- 在 Thread-2 上锁的过程中,如果 Thread-3,Thread-4,Thread-5 也来执行 synchronized(obj),就会进入 EntryList BLOCKED
- Thread-2 执行完同步代码块的内容,然后唤醒 EntryList 中等待的线程来竞争锁,竞争的时是非公平的
- 图中 WaitSet 中的 Thread-0,Thread-1 是之前获得过锁,但条件不满足进入 WAITING 状态的线程,后面讲 wait-notify 时会分析
注意:
- synchronized 必须是进入同一个对象的 monitor 才有上述的效果
- 不加 synchronized 的对象不会关联监视器,不遵从以上规则
Monitor 工作原理 字节码角度
1 | static final Object lock = new Object(); |
- getstatic #2 拿到lock锁的对象的引用,将来会关联monitor。
- dup 复制了一份
- astore_1 存储到slot 1中,为了将来解锁用
- monitorenter 将lock对象MarkWord置为Monitor指针
- monitorexit是充值MarkWord,唤醒EntryList让线程能够重新竞争锁。
- 如果第6到16行出现问题,会到第19行执行,astore_2是将异常对象e存放到slot 2中。
- 第20行是找到lock对象的引用地址,第21行是重置MarkWord,唤醒EntryList,第23行athrow是抛出处理不了的异常。

1 | public static void main(java.lang.String[]); |
小结:
monitorenter和monitorexit是 JVM 原语,用于管理锁的加解- 所有的锁重入、等待唤醒等功能,都是 JVM 依赖 Monitor 来实现的
- 方法上使用
synchronized,在字节码中体现为 ACC_SYNCHRONIZED 标记,不显示字节码指令
| 注意点 | 说明 |
|---|---|
synchronized(obj) 会触发 Monitor 机制 |
对象头中的 Mark Word 会存储指向 Monitor 的指针 |
| 只有锁对象才与 Monitor 绑定 | 普通对象不会默认拥有 Monitor |
| Monitor 中的 EntryList 和 WaitSet 是不同的 | EntryList 是“还没获得锁的”,WaitSet 是“拿过锁但进入 wait 的” |
| Monitor 的竞争是非公平的 | 谁被唤醒并不一定是排队最久的线程 |
编译为字节码后表现为 monitorenter / monitorexit |
且会生成异常处理逻辑以避免锁泄露 |
synchronized 优化原理(小故事)
打印机共享队列模型
背景:
你们公司有一台共享打印机(表示临界资源),程序员小王和其他同事每天都要用它打印资料。为了不冲突,公司安排了三种打印控制机制来「优化效率」,正好对应 JVM 中的三种锁状态。
锁优化三种形态对比类比
| JVM 锁类型 | 类比打印控制机制 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| 偏向锁(Biased) | 打印机记住上一个用户是谁 如果是同一个人再次使用,不做任何检查,直接打印 | 无竞争时性能最好(零开销) |
| 轻量级锁(Lightweight) | 多人要打印,先排队轮询查看是否空闲,只要打印机还没结束上一个人的工作,就自旋等待几次 | 低冲突下仍能保持高性能(无阻塞) |
| 重量级锁(Heavyweight) | 冲突太多了,打印任务就被挂起/唤醒,由操作系统调度谁先打印 | 冲突激烈时保障正确性,但性能最差 |
场景详解
偏向锁(Biased Lock)
- 小王是第一个用打印机的人
- 打印机会记住小王的身份
- 后面只要小王再次来打印,打印机就直接开工,不检查排队系统,因为它“偏向”小王
就像对象 MarkWord 中记录了某个线程的 ID,只有当其他线程来竞争才撤销偏向锁
轻量级锁(Lightweight Lock)
- 小王打印时,小李也来了
- 打印机会说:“先别挂起,等等看小王是不是很快结束”
- 小李就在打印机旁边“自旋等待”
- 如果小王很快结束了,小李就立即上,没有阻塞、也没有上下文切换
自旋锁本质:用 CPU 忙等来换取线程不挂起
重量级锁(Heavyweight Lock)
- 现在来了十几个人都要打印,等太久了
- 打印机会说:“别等了,我排个队号,通知你们一个个来”
- 系统就开始用 阻塞 → 唤醒 → 再阻塞的方式调度线程
操作系统介入调度,线程切换代价高,效率最低
最后总结:
| 情况 | JVM锁 | 打印类比 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 单线程使用资源 | 偏向锁 | 打印机只认上一次的使用者 | 零开销,最快 |
| 少量线程争用 | 轻量级锁 | 排队观察是否释放 | 快速尝试获取锁 |
| 多线程激烈争用 | 重量级锁 | 线程挂起等待系统调度 | 安全但慢 |
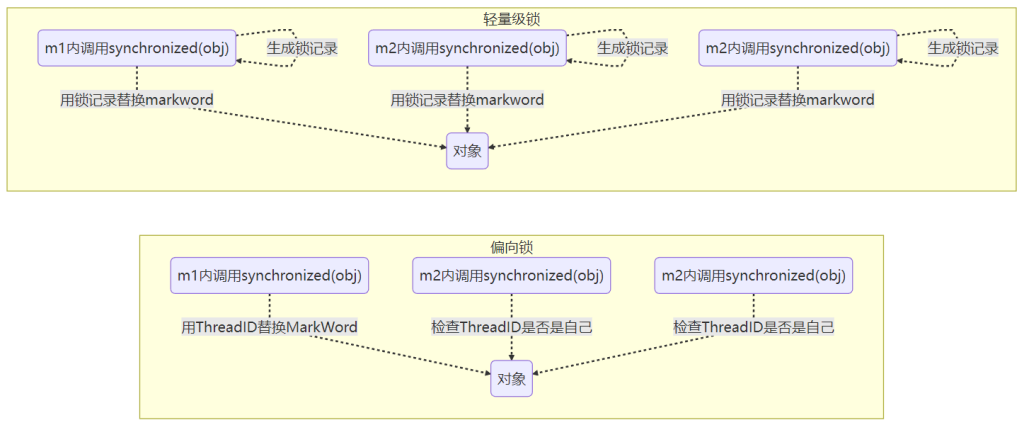
synchronized 优化原理 轻量级锁
使用背景
轻量级锁的应用场景:
当多个线程访问同一个对象的 synchronized 同步代码,但这些访问是错开的、无真正竞争,就可以使用轻量级锁优化性能。
轻量级锁的关键特点
| 特性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
语法上与 synchronized 一致 |
对程序员完全透明,无需改变写法 |
| 避免线程阻塞 | 利用 CAS + 自旋 替代传统阻塞/唤醒机制 |
| 自动升级为重量级锁 | 若发生竞争,自动进入锁膨胀流程 |
轻量级锁加锁流程(配图讲解):
1 | static final Object obj = new Object(); |
1.创建锁记录 Lock Record
- 每个线程的栈帧中维护 Lock Record
- 结构中包含:
- 锁定对象引用
- 原始 Mark Word 的备份
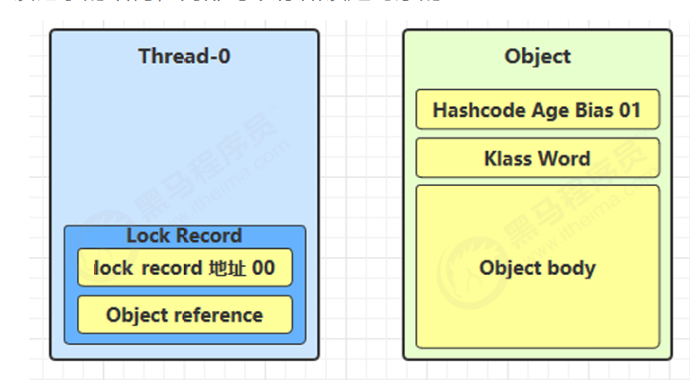
2.CAS 尝试替换对象头 Mark Word
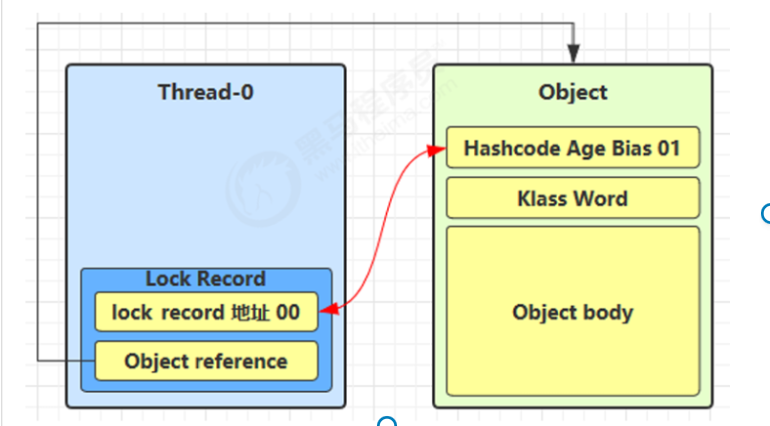
使用 CAS(原子操作)将锁对象的 Mark Word 替换为指向线程中 Lock Record 的指针(让锁记录里的“lock record 地址 00”和锁对象里的“Hashcode Age Bias 01”进行交换。交换是为了表示加锁。)
如果成功:说明当前线程成功加锁
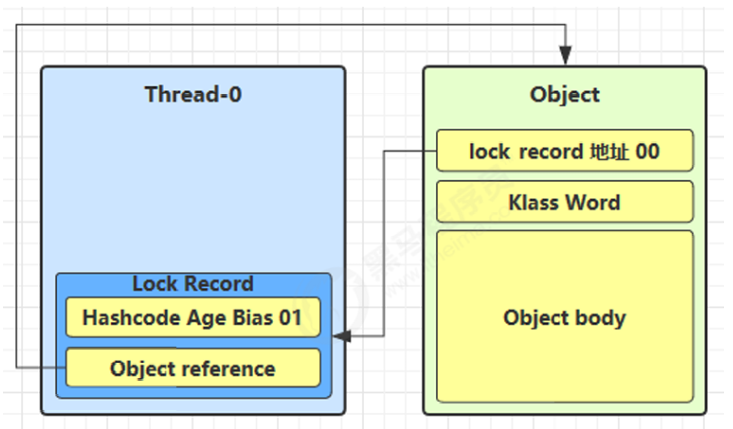
📌 此时对象头的状态变为:
Mark Word → Lock Record 地址 + 状态 00(表示轻量级锁)
3.CAS 加锁失败的两种情况
情况1:其他线程已持有锁
- 说明产生了真实竞争
- JVM 会执行锁膨胀(升级为重量级锁)
情况2:重入(同一个线程重复加锁)
- 当前线程再增加一个 Lock Record,表示重入一次
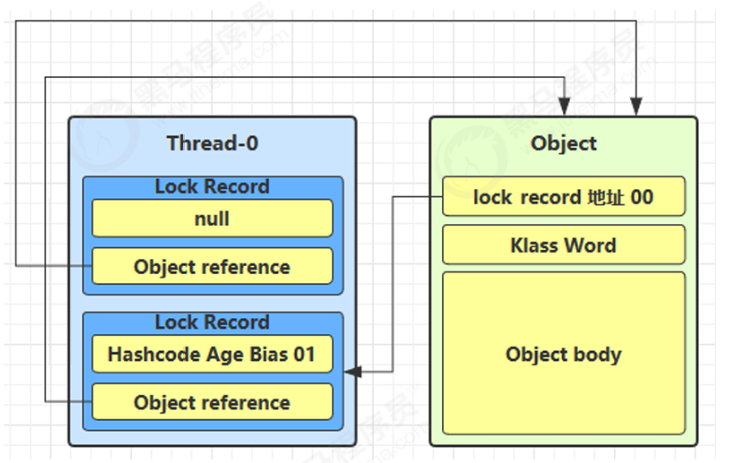
4.轻量级锁解锁过程
情况1:锁记录顶部是 null(说明是重入)
- 直接出栈,减少重入计数
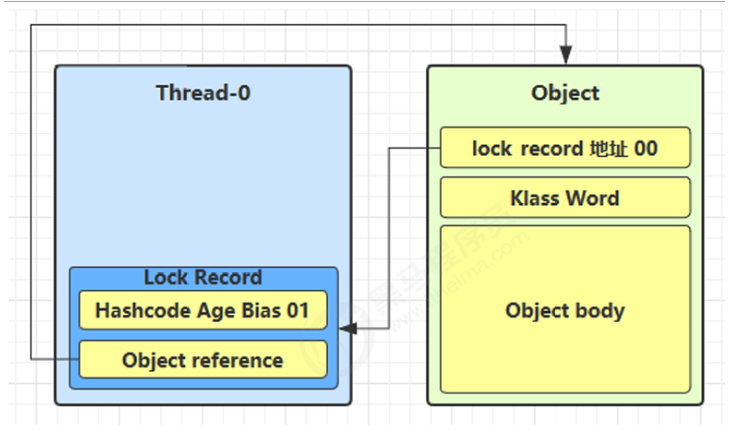
情况2:锁记录不为 null(正常解锁)
- 使用 CAS 将 Mark Word 恢复到原值(即恢复对象头)
| 结果 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| CAS 成功 | 解锁成功,保持轻量级状态 |
| CAS 失败 | 已膨胀为重量级锁,进入重量级解锁流程 |
轻量级锁 vs 重量级锁 性能对比
| 特点 | 轻量级锁 | 重量级锁 |
|---|---|---|
| 无线程竞争 | 开销极小(无阻塞) | 基本等价 |
| 少量竞争 | 自旋等待,高性能 | 线程阻塞 + 上下文切换 |
| 激烈竞争 | 自动升级(膨胀) | 线程挂起/唤醒效率低 |
总结:轻量级锁原理核心要点
| 流程 | 机制 |
|---|---|
| 加锁 | CAS 替换对象头 Mark Word → 指向 Lock Record |
| 重入 | 新增 Lock Record 入栈 |
| 解锁 | CAS 恢复 Mark Word 原值 |
| 失败 | 说明锁已膨胀,进入重量级锁逻辑 |
锁升级
升级过程
synchronized 是可重入、不公平的重量级锁,所以可以对其进行优化
1 | 无锁 -> 偏向锁 -> 轻量级锁 -> 重量级锁 // 随着竞争的增加,只能锁升级,不能降级 |
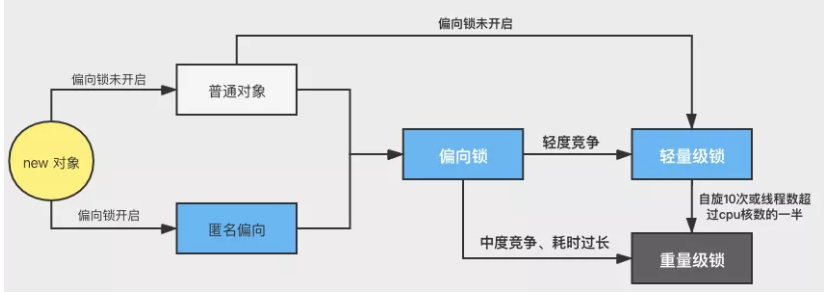
锁膨胀
什么是锁膨胀?
锁膨胀是指:
当线程尝试加轻量级锁失败(即 CAS 操作失败)时,JVM 会将锁升级为重量级锁(Monitor 锁),以保证多线程环境下的互斥访问。
1 | static final Object obj = new Object(); |
假设有两个线程:
- Thread-0:首先成功加上了轻量级锁(CAS 成功)
- Thread-1:此时也尝试对同一个
obj加锁,但由于 Thread-0 已加锁,CAS 失败
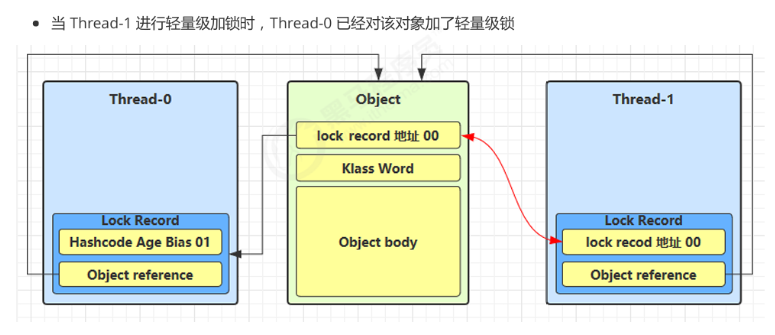
加锁失败 → 锁膨胀流程如下
1️⃣ Thread-1 加锁失败,触发锁膨胀:
- JVM 为该
obj对象分配一个 Monitor 对象 obj对象头的 Mark Word 被修改:由轻量级锁状态 → 指向 Monitor 地址 + 状态为重量级锁(10)
2️⃣ Thread-1 进入 Monitor 的 EntryList
- Thread-1 无法立即获取锁,被挂起
- 加入到 Monitor 的 EntryList(阻塞队列)
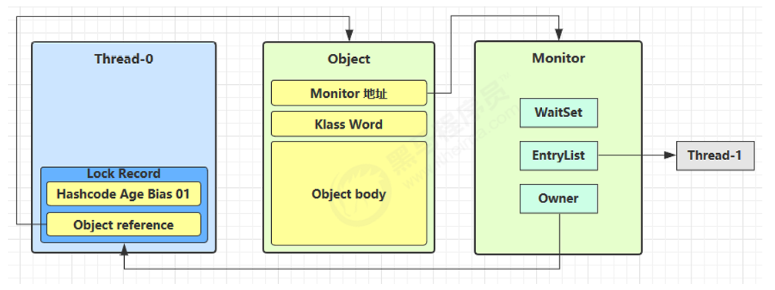
解锁时的行为(Thread-0 解锁)
3️⃣ Thread-0 执行完同步块,尝试解锁:
- 原本会用 CAS 恢复 Mark Word,但此时对象头指向了 Monitor(即锁已膨胀)
- CAS 解锁失败,说明锁已升级为重量级
4️⃣ 进入重量级解锁流程:
- 找到 Monitor 对象
- 将 Owner 设置为
null - 唤醒 EntryList 中的线程(如 Thread-1),重新尝试获取锁
| 阶段 | 行为 |
|---|---|
| 加锁失败 | CAS 不成功 → JVM 自动膨胀锁 |
| 膨胀后 | 对象头不再保存轻量锁引用,而是直接指向 Monitor |
| 解锁时 | 通过 Monitor 解锁,唤醒其他等待线程 |
注:
| 点 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 锁膨胀是自动的 | 不需要程序员介入,由 JVM 维护 |
| 一旦膨胀不可降级 | 对象锁膨胀为重量级后,不会恢复为轻量或偏向锁,除非 GC 回收后重新创建对象 |
| 性能影响大 | 线程挂起和唤醒涉及系统调用,代价高,因此 应尽量避免激烈竞争,否则性能下降显著 |

自旋优化
1.为什么要自旋?
当线程尝试加锁时,如果发现锁已被其他线程持有,默认行为是:阻塞等待。
问题:阻塞带来开销
- 线程阻塞/唤醒都需要进入内核态,代价非常大(上下文切换、队列维护等)
优化方式:自旋等待
- 如果持锁线程马上就会释放锁,那我就“等一下”看看能不能直接拿到锁,避免被挂起
这就是自旋锁的核心思想。
2.什么是自旋锁?
自旋锁是一种非阻塞的锁优化方式:线程在短时间内反复尝试获取锁,而不是立即挂起自己。
- “自旋” = 在 CPU 上循环尝试(使用
while+ CAS) - 若自旋期间锁被释放,当前线程立即拿到锁,成功执行
- 若多次尝试仍未成功 → 最终还是会挂起
3.自旋成功 VS 自旋失败(对照流程)
自旋成功
| 线程1 ( core 1上) | 对象Mark | 线程2 ( core 2上) |
|---|---|---|
| - | 10(重量锁) | - |
| 访问同步块,获取monitor | 10(重量锁)重量锁指针 | - |
| 成功(加锁) | 10(重量锁)重量锁指针 | - |
| 执行同步块 | 10(重量锁)重量锁指针 | - |
| 执行同步块 | 10(重量锁)重量锁指针 | 访问同步块,获取 monitor |
| 执行同步块 | 10(重量锁)重量锁指针 | 自旋重试 |
| 执行完毕 | 10(重量锁)重量锁指针 | 自旋重试 |
| 成功(解锁) | 01(无锁) | 自旋重试 |
| - | 10(重量锁)重量锁指针 | 成功(加锁) |
| - | 10(重量锁)重量锁指针 | 执行同步块 |
| - | … | … |
避免了挂起和唤醒的系统开销
自旋失败
| Thread-1(core1) | 对象Mark Word | Thread-2(core2) |
|---|---|---|
| 长时间持有同步块 | 重量锁指针(10) | 进入自旋 |
| 仍未释放 | 重量锁指针(10) | 自旋多次 → 仍失败 |
| - | - | 进入阻塞,排队等待 |
这种情况会先浪费 CPU,再进入阻塞 ➜ 所以自旋也有代价
4.自旋锁的适用场景
| 条件 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 多核 CPU | 否则“自旋”会让 CPU 空转,得不偿失 |
| 线程持锁时间短 | 适合 “临界区执行时间短” 的场景 |
| 有机会快速获取锁 | 否则就应该直接阻塞等待 |
5.JVM 自旋锁机制细节
- Java 6 起引入自适应自旋锁
- 自旋次数不是固定的,而是动态调整
| 状况 | JVM策略 |
|---|---|
| 上次自旋成功 | 下次增加自旋次数(更有希望成功) |
| 上次自旋失败 | 下次减少或不自旋 |
JVM 自主判断是否值得“等一下”,不由程序员控制自旋开关(Java 7+ 以后)
总结:
| 点 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 自旋锁是一种乐观锁 | 先尝试获取,不成功再阻塞 |
| 避免了上下文切换开销 | 提高了轻量竞争下的效率 |
| 失败后仍需挂起 | 所以不能滥用,适合“短期持锁” |
| JVM 自动控制自旋行为 | 编程时只需使用 synchronized,无需手动控制 |
synchronized 优化原理 偏向锁
1.什么是偏向锁?
偏向锁是一种在无竞争场景下优化的轻量锁机制,适用于单线程反复加锁的场景。
Java 6 引入偏向锁来减少 synchronized 的 CAS 操作开销:
- 如果一个线程获取了对象锁,就将它的 线程 ID 记录在对象的 Mark Word 中;
- 之后这个线程再次加锁该对象时,只需要判断 Mark Word 中的 ID 是不是自己;
- 是自己的话,就跳过 CAS 操作,直接进入临界区;
- 所以只要没有其他线程竞争,这个对象就偏向于当前线程。
2.代码示例
1 | public static void m1() { |
偏向锁:
- 第一次加锁:通过 CAS 设置 Mark Word 中的线程 ID;
- 之后 m2、m3 中重复加锁,只需比较 ID → 是自己 → 直接执行;
- ✅ 无需 CAS,所以性能更好。
轻量级锁:
- 每次进入 synchronized 都要创建锁记录 Lock Record;
- 每次都要做 CAS 操作 → 替换 Mark Word;
- 相比偏向锁,多了不必要的 CAS。
3.Mark Word 状态变化(对象头)
偏向锁的关键在于 Mark Word 中记录线程 ID,下面是几种状态的二进制结构:
| 状态 | 描述 | 标识位 |
|---|---|---|
| 普通对象 | 未加锁 | 01 |
| 偏向锁 | Mark Word 中存线程ID | 01 + biased=1 |
| 轻量级锁 | Mark Word 指向锁记录地址 | 00 |
| 重量级锁 | 指向 Monitor 对象 | 10 |
| GC标记 | 标记为垃圾回收 | 11 |
4.常见偏向锁测试实验总结
1️⃣ 开启偏向锁(默认延迟)
- JVM 默认延迟几秒开启偏向锁(为避免类加载过程影响)
- 可加 VM 参数
-XX:BiasedLockingStartupDelay=0立即开启
2️⃣ 查看偏向锁加锁效果
借助 jol 工具查看对象头:
1 | Dog d = new Dog(); |
- synchronized 前后 Mark Word 是否改变;
- 可看到线程 ID 写入对象头,重复进入锁不再更改。
3️⃣ 禁用偏向锁:-XX:-UseBiasedLocking
- 对象头中不会出现线程 ID
- 会直接走轻量级锁逻辑
5.偏向锁的撤销情况(发生线程竞争)
以下情况会导致偏向锁撤销:
| 情况 | 结果 |
|---|---|
调用 hashCode() |
对象 Mark Word 必须存 hashcode,线程 ID 就放不下了 |
| 其他线程尝试加锁 | 偏向锁撤销,升级为轻量级锁(有竞争了) |
使用 wait/notify |
JVM 会自动撤销偏向锁 |
| JVM 达到撤销偏向锁的阈值 | 会批量撤销 |
6.偏向锁的“批量行为”
偏向锁本质是“对象偏向某个线程”,但是当大量对象频繁发生线程切换(即偏向锁不断被撤销)时,JVM 会触发优化机制:
| 名称 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| 重偏向(Rebias) | 将偏向锁从旧线程切换为新线程(若没有真实竞争) |
| 批量撤销(Bulk Revoke) | 彻底放弃偏向锁,整个类的实例以后都不再启用偏向 |
1)重偏向(Rebias)
- 如果发现对象虽然换线程了,但没有真正竞争(只是不同线程加锁);
- JVM 会重偏向新线程;
- 默认最多支持 20 次撤销后,尝试重偏向新线程。
1 | public class TestBiased1 { |
解读流程:
| 阶段 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| t1 线程创建对象并加锁 | 每个 dog 对象被偏向 t1,Mark Word 中记录了 t1 的线程 ID |
| t2 线程尝试加锁 | 发现 Mark Word 是 t1 的 ID,但当前线程是 t2,不匹配 |
| JVM 判断是否存在真正竞争? | 没有。只有 t2 在使用,t1 已结束,不是多线程竞争 |
| JVM 执行“重偏向”(rebias) | 将 dog 对象的偏向线程 ID 改为 t2 的 ID,避免升级为轻量级锁 |
| 重偏向默认最多 20 次 | 超过则不会继续 rebias,会尝试触发下一阶段:批量撤销 |
✅ 最终效果:对象仍保持偏向锁状态,只是从 t1 变成 t2,避免升级,提高性能。
2)批量撤销(Bulk Revoke)
- 当撤销偏向锁超过 40 次(阈值);
- JVM 判定“这类对象根本就不该偏向”;
- 整个类的对象都会禁用偏向锁,以后新建的对象也不再偏向。
1 | public class TestBiased2 { |
解读流程:
| 阶段 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 前 20 次 | t2 尝试访问 t1 偏向的对象,触发 rebias |
| 第 21~40 次 | JVM 判断 rebias 效果不好,继续尝试偏向切换 |
| 第 41 次 | 超过了 JVM 的容忍上限(默认是 40 次) |
| JVM 决策 | 执行 批量撤销,对 Dog 这个类的所有实例取消偏向锁功能 |
| 后续所有 new Dog() 对象 | 直接跳过偏向锁阶段,初始就是轻量级锁或普通无锁状态 |
🚫 批量撤销是不可逆的,该类所有实例将不再享受偏向锁优化。
7.重偏向 vs 批量撤销
| 项目 | 重偏向(Rebias) | 批量撤销(Bulk Revoke) |
|---|---|---|
| 触发条件 | 偏向锁撤销不含真实竞争(切线程) | 偏向锁撤销超过阈值(默认 40 次) |
| 结果 | 将偏向锁从旧线程迁移到新线程 | 类级别禁用偏向锁 |
| 性能影响 | 优化,避免不必要升级 | 之后对象不再使用偏向锁,性能退化 |
| 可逆性 | 可继续重偏向 | 不可逆,彻底关闭偏向锁 |
8.总结:偏向锁核心知识点
| 项目 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 引入目的 | 减少无竞争场景下的 CAS,提升性能 |
| 适用场景 | 同一线程反复加锁对象 |
| 优点 | 性能最优,完全无竞争时零开销加锁 |
| 缺点 | 遇到 hashCode、多线程、wait/notify 后自动撤销 |
| 撤销后升级 | 偏向锁 → 轻量级锁 → 重量级锁(如有阻塞) |
| 自适应行为 | 20次尝试后重偏向;40次失败后批量撤销 |
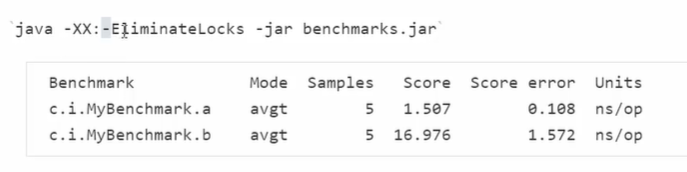
锁消除

JIT即时编译器会发现o这个对象只有在b方法中使用,没有其它的地方用到,所以加这个锁毫无意义,因此在字节码中会把加锁的代码去掉。
在启动jvm的时候加入如下参数,会关闭这种锁消除优化,然后会发现性能的差距比较明显:
4.8Java 锁优化全过程图谱(偏向锁 → 轻量级锁 → 重量级锁的完整演化链路)
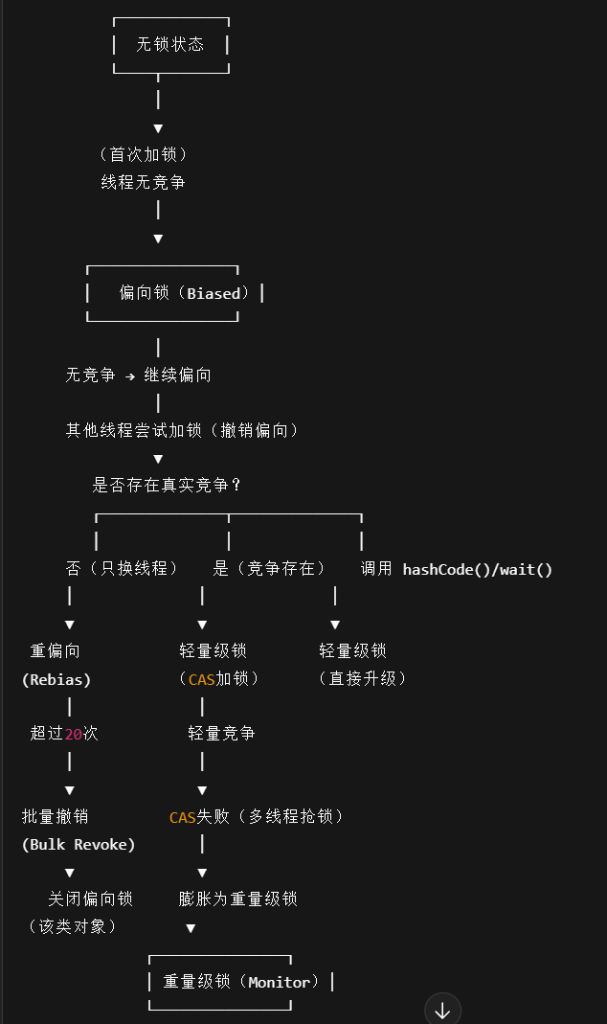
各锁状态关键点
| 锁类型 | 加锁方式 | 特点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 无锁 | 无加锁 | 并发不访问,共享安全 | 单线程对象 |
| 偏向锁 | 修改 Mark Word 保存线程ID | 无CAS操作,性能最好 | 单线程反复加锁 |
| 轻量级锁 | CAS + Lock Record | 自旋获取,性能较高 | 少量线程竞争 |
| 重量级锁 | Monitor + EntryList | 阻塞等待、上下文切换代价高 | 高并发场景 |
锁状态变化触发条件
| 当前状态 | 触发条件 | 变更后的状态 |
|---|---|---|
| 偏向锁 | 另一个线程访问,无竞争 | 重偏向(20次以内) |
| 偏向锁 | 另一个线程访问 + 超过20次 | 批量撤销 |
| 偏向锁 | hashCode / wait 等操作 | 轻量级锁 |
| 轻量级锁 | CAS失败(存在真实竞争) | 重量级锁 |
| 重量级锁 | 锁持有线程执行完或解锁 | 所有线程恢复运行 |
Mark Word 状态位说明(低2位)
| 状态 | Mark Word标志位 | 内容概括 |
|---|---|---|
| 无锁 | 01 |
可存 hashCode / GC 等 |
| 偏向锁 | 01 + biased=1 |
保存线程ID |
| 轻量级锁 | 00 |
指向 Lock Record 的地址 |
| 重量级锁 | 10 |
指向 Monitor 的地址 |
| GC标记 | 11 |
GC相关 |
总结:三种优化策略对比
| 优化策略 | 核心目的 | 使用方式(对程序员) | 性能表现 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 偏向锁 | 减少CAS操作 | 默认启用 | 最快 |
| 轻量级锁 | 避免阻塞/唤醒 | 默认启用 | 中等 |
| 自旋 + 膨胀 | 让线程先等等看 | 自动控制 | 中等偏慢 |
| 重量级锁 | 最后兜底(保证正确) | 自动进入 | 最慢 |
4.9wait notify
wait方法可以理解为让线程进入休息室等待,然后让其它线程继续工作。
当另一个线程调用notify会将wait方法的线程唤醒。
wait / notify原理
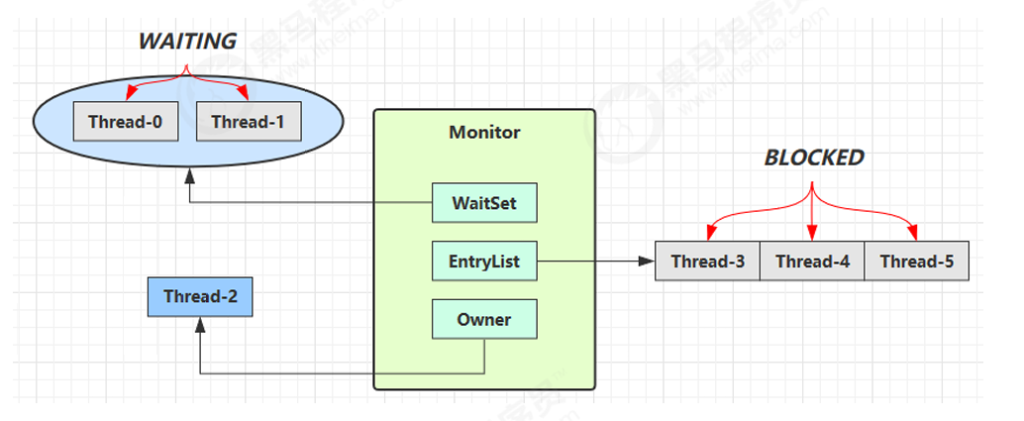
- Owner 线程发现条件不满足,调用 wait 方法,即可进入 WaitSet 变为 WAITING 状态
- BLOCKED 和 WAITING 的线程都处于阻塞状态,不占用 CPU 时间片
- BLOCKED 线程会在 Owner 线程释放锁时唤醒
- WAITING 线程会在 Owner 线程调用 notify 或 notifyAll 时唤醒,但唤醒后并不意味者立刻获得锁,仍需进入 EntryList 重新竞争
API 介绍
obj.wait()让进入 object 监视器的线程到 waitSet 等待obj.notify()在 object 上正在 waitSet 等待的线程中挑一个唤醒obj.notifyAll()让 object 上正在 waitSet 等待的线程全部唤醒
要注意一点,某个线程要先成为Owner,才有资格进入WaitSet。
只有某个线程成为Owner,才有资格唤醒WaitSet中的线程。
它们都是线程之间协作的手段,都属于Object对象的方法。必须获得此对象的所,才能调用这几个方法。
1 | @Slf4j(topic = "c.TestWaitNotify") |

无参的wait,默认传入0,表示无限等待。

带参的wait,比如wait(1000),就是只等待1秒,如果等不到唤醒,就继续往下执行。

wait vs sleep
sleep(long n) 和 wait(long n) 的区别
- API角度上sleep 是 Thread 方法,而 wait 是 Object 的方法
- sleep 不需要强制和 synchronized 配合使用,但 wait 需要和 synchronized 一起用
- sleep 在睡眠的同时,不会释放对象锁的,但 wait 在等待的时候会释放对象锁
相同点:
- 1.均可响应中断
- 2.sleep(long)和wait(long)进入TimedWaiting状态,但wait()会进入Waiting状态
1 | @Slf4j(topic="c.Test19") |
wait notify正确使用姿势
我们设定一个“干活”场景,有两个人物:
- 小南(干活需要烟 🧷)
- 小女(干活需要外卖 🍔)
他们要等“送烟的”或“送外卖的”线程送来对应资源才能开始干活。
step 1-sleep 方式阻塞等待(错误做法)
某个线程调用sleep,会导致仍然带着锁没释放,别的线程会被阻塞,需要干等着,导致效率低。
1 | new Thread(() -> { |
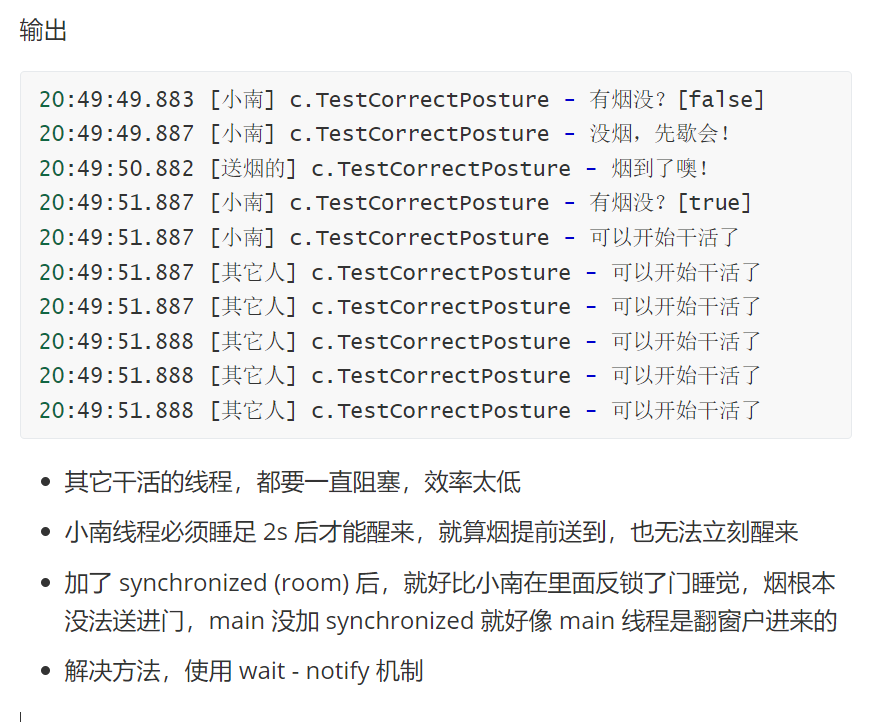
sleep()不会释放锁- 其它线程(“送烟的”、“其它人”)进不来 → 全部阻塞
- 并发性能极差
step 2-用 wait + notify(初步优化)
思考下面的实现行吗,为什么?
1 | new Thread(() -> { |

- 改进点:
wait()会释放锁,notify()唤醒后再继续执行- 别的线程就能进来干活或送资源了
- 潜在问题:
- 如果多个线程在
wait(),notify()只随机唤醒一个线程,可能唤醒错误人(虚假唤醒)
step 3-多个线程使用 wait + notify(虚假唤醒问题)
1 | new Thread(() -> { |
输出
1 | 20:53:12.173 [小南] c.TestCorrectPosture - 有烟没?[false] |
- notify 只能随机唤醒一个 WaitSet 中的线程,这时如果有其它线程也在等待,那么就可能唤醒不了正确的线程,称之为【虚假唤醒】
- 解决方法,改为 notifyAll
step 4-改用 notifyAll(全部唤醒)
1 | new Thread(() -> { |
输出
1 | 20:55:23.978 [小南] c.TestCorrectPosture - 有烟没?[false] |
- 用 notifyAll 仅解决某个线程的唤醒问题,但使用 if + wait 判断仅有一次机会,一旦条件不成立,就没有重新判断的机会了
- 解决方法,用 while + wait,当条件不成立,再次 wait
step 5-最终正确姿势 → while + wait + notifyAll
将 if 改为 while
1 | if (!hasCigarette) { |
改动后
1 | while (!hasCigarette) { |
输出
1 | 20:58:34.322 [小南] c.TestCorrectPosture - 有烟没?[false] |
总结:wait / notify 正确使用姿势
| 要点 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 必须持有锁对象 | wait/notify 只能在 synchronized(lock) 内部使用 |
| wait 释放锁 | wait() 会释放锁 → 允许其他线程进入同步块 |
| notify 不释放锁 | notify() 只是把线程唤醒,但还要等锁释放才真正继续 |
| 虚假唤醒 | 被错误唤醒,不等于条件已满足 |
| 用 while 代替 if | 醒来后重新判断条件,避免出错 |
| notifyAll 最安全 | 通常比 notify 更稳妥,尤其多个条件/线程时 |
4.10设计模式
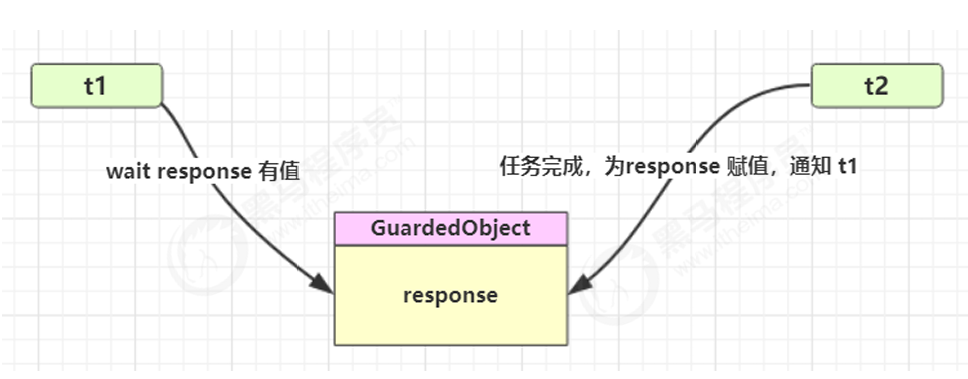
同步模式之保护性暂停(Guarded Suspension) 定义
保护性暂停是一种线程间同步模式:一个线程等待另一个线程的结果,并在结果就绪时继续运行。
关键点:
- 一方等待结果(消费者)
- 一方产生结果(生产者)
- 两者通过
GuardedObject关联 - 属于同步模式的一种
要点:
1.有一个结果需要从一个线程传递到另一个线程,让他们关联同一个GuardedObject。
2.如果有结果不断从一个线程到另一个线程那么可以使用消息队列(见生产者/消费者)。
3.JDK中join的实现、Future的实现,采用的就是此模式。
4.因为要等待另一方的结果,因此归类到同步模式。
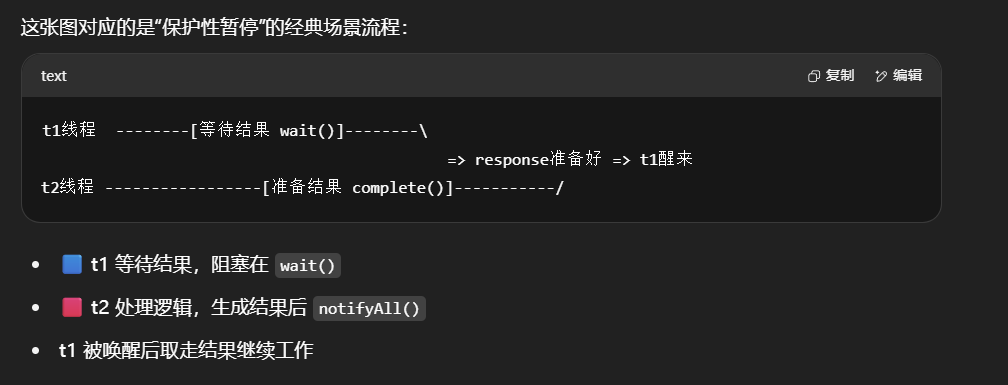
保护性暂停 实现
t1等待GuardedObject中response的值,t2为response赋值,会通知t1。
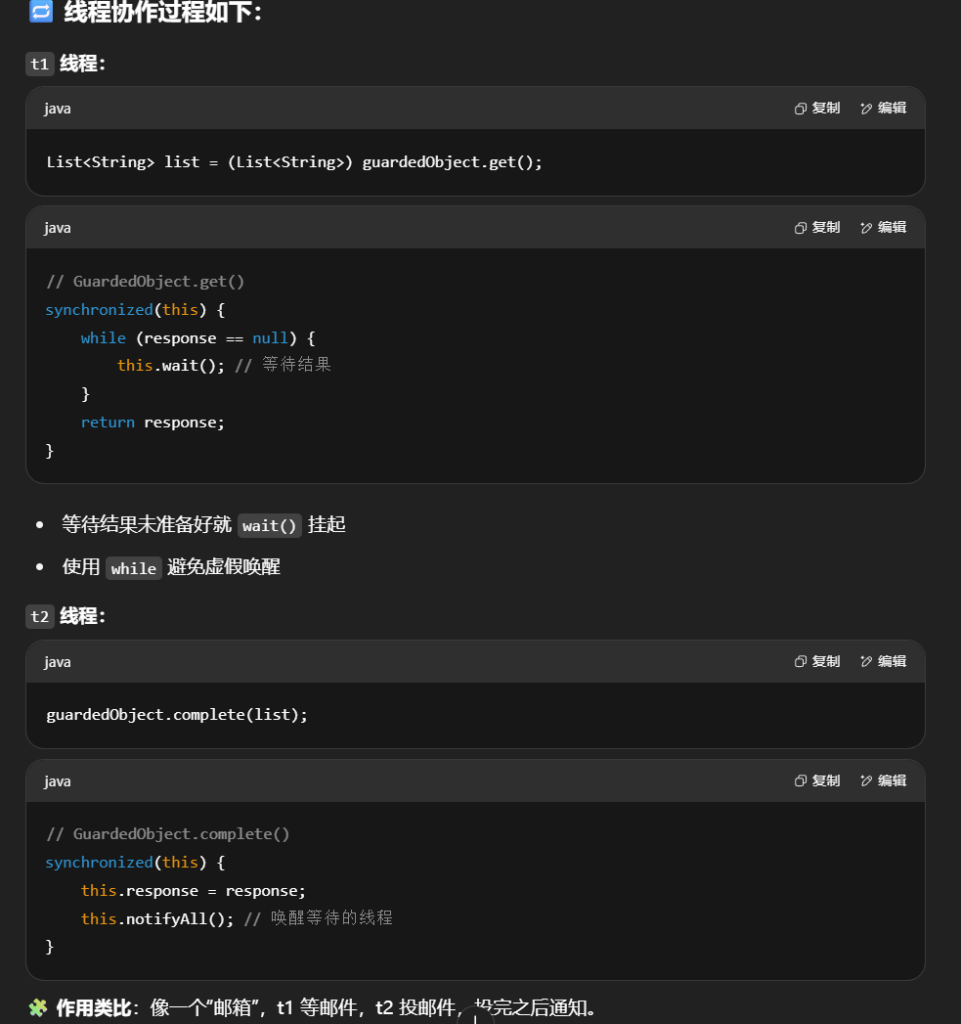
下面程序的思路是:t2线程会调用Downloader的download方法下载资源,complete方法用于给成员变量赋值,然后通知所有线程。t1线程会调用get方法获取成员变量的值,如果成员变量没有值就wait等待,获取到值后打印代码行数。
1 | (topic = "c.Test20") |
- 线程 t1:调用
get()等待结果 - 线程 t2:调用
complete()提供结果,并notifyAll()唤醒 t1
保护性暂停- 扩展 增加超时
首先考虑2点:
1.设置超时事件后如何退出while循环:判断当前时间是否大于所设定的超时来判断。
2.虚假唤醒问题,假如wait方法中传入的参数是timeout,假如线程在前一次被唤醒,参数还没准备好,在此休眠仍然会有2秒的超时时间,不符合要求。必须是timeout减去之前经过的时间。
加入超时机制的原因:
- 避免线程“无限等待”
- 同时应对虚假唤醒(即线程醒了,但结果还没来)
1 | public Object get(long timeout){ |
保护性暂停 扩展 增加超时 测试
修改main代码如下,模拟虚假唤醒的情况(唤醒了但数据没准备好):
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |

- t1 发起 get(timeout=2000)
- 若 2s 内未收到结果,则返回 null
- 即使中间被提前唤醒(虚假唤醒),也会根据实际 elapsed time 重新计算剩余等待时间
设计模式 join原理
是调用者轮询检查线程 alive 状态
1 | t1.join(); |
等价于下面的代码
1 | synchronized (t1) { |
注意
join 体现的是【保护性暂停】模式,请参考之
源码:
1 | //不带参 |
设计模式 保护性暂停 扩展 解耦等待和生产
场景需求:
多个线程各自等待不同的结果(收信),不能都用同一个 GuardedObject。
分析
如果需要在多个类之间使用GuardedObject对象,作为参数传递不是很方便,因此设计一个用来解耦的类,这样不仅能够解耦结果等待者和结果生产者,还能够同时支持多个任务的管理。
解法:Mailboxes 解耦
1 | Map<Integer, GuardedObject> boxes |
- 每个收信人(线程)创建独立的
GuardedObject - 每个投信人(线程)通过
id投递指定内容
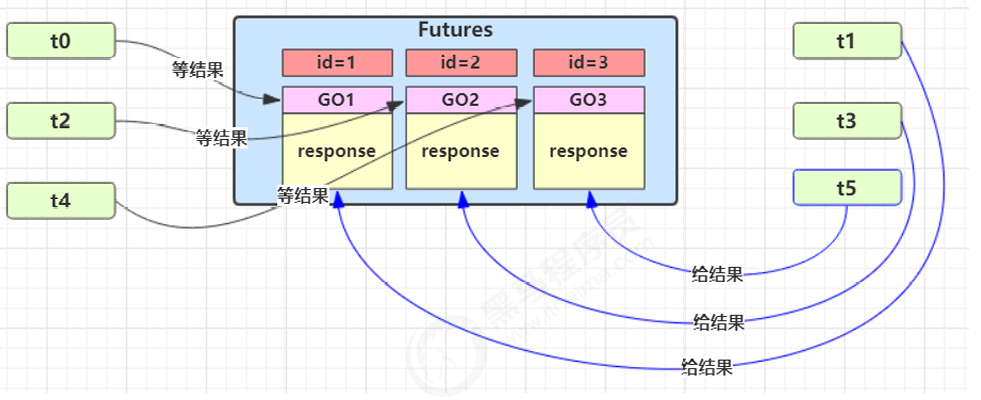
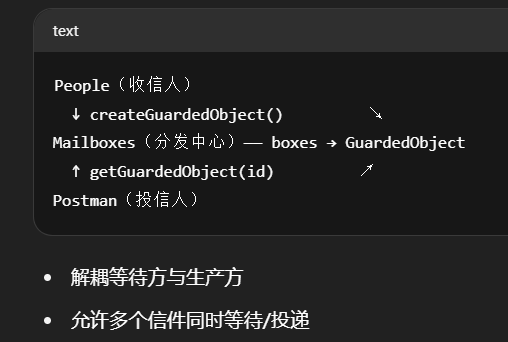
实现:
1 |
|
测试

- 每个
People创建各自信箱 - 每个
Postman精准投信 - 无锁争用、无阻塞冲突,实现并发收发信
总结:保护性暂停核心精要
| 要点 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 本质 | 一个线程等待另一个线程的结果 |
| 工具 | synchronized + wait/notifyAll |
| 必备 | 用 while 包住 wait(),防止虚假唤醒 |
| 扩展 | 加入超时、解耦多个任务的等待和通知 |
| 应用 | Future, join(), 异步RPC, 邮箱系统 |
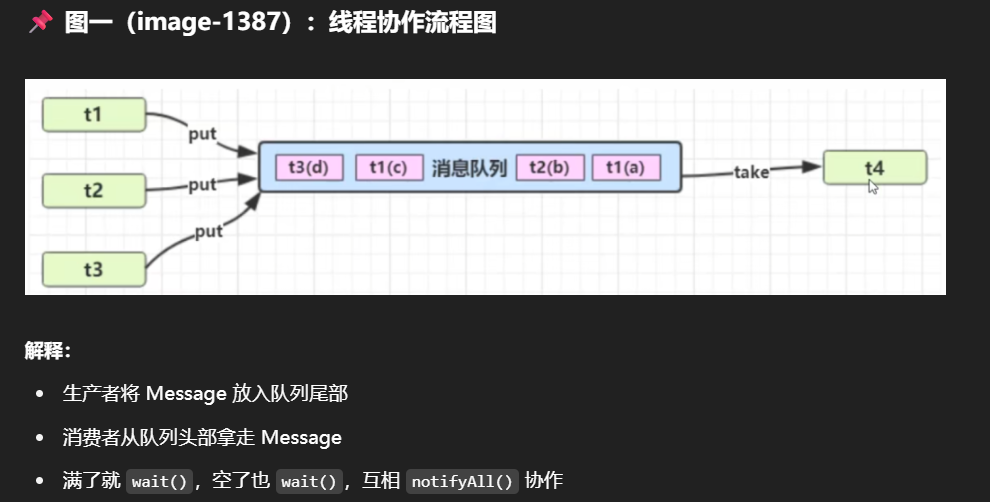
设计模式-异步模式之生产者消费者 定义
什么是生产者-消费者模式?
定义:
一种异步线程协作模型,生产者线程负责生成数据,消费者线程负责处理数据。通过一个阻塞队列(消息队列)在两者之间进行解耦。
要点
- 与前面的保护性暂停中的 GuardObject 不同,不需要产生结果和消费结果的线程一一对应((比如之前的保护性暂停中要求1个居民要配1个快递员,如果有几百个居民,则需要配几百个快递员))
- 消费队列可以用来平衡生产和消费的线程资源
- 生产者仅负责产生结果数据,不关心数据该如何处理,而消费者专心处理结果数据
- 消息队列是有容量限制的,满时不会再加入数据,空时不会再消耗数据
- JDK 中各种阻塞队列,采用的就是这种模式
与保护性暂停的区别
| 项目 | 保护性暂停 | 生产者-消费者 |
|---|---|---|
| 一对一模型 | 是 | 否(可多对多) |
| 是否异步 | 同步结果处理 | 异步投递处理 |
| 是否等待匹配线程 | 是 | 否 |
| 是否支持缓存 | 否 | ✅ 支持队列缓存 |
| 应用场景 | 等待一个特定任务响应 | 数据流式处理,任务解耦 |
设计模式 生产者消费者 实现
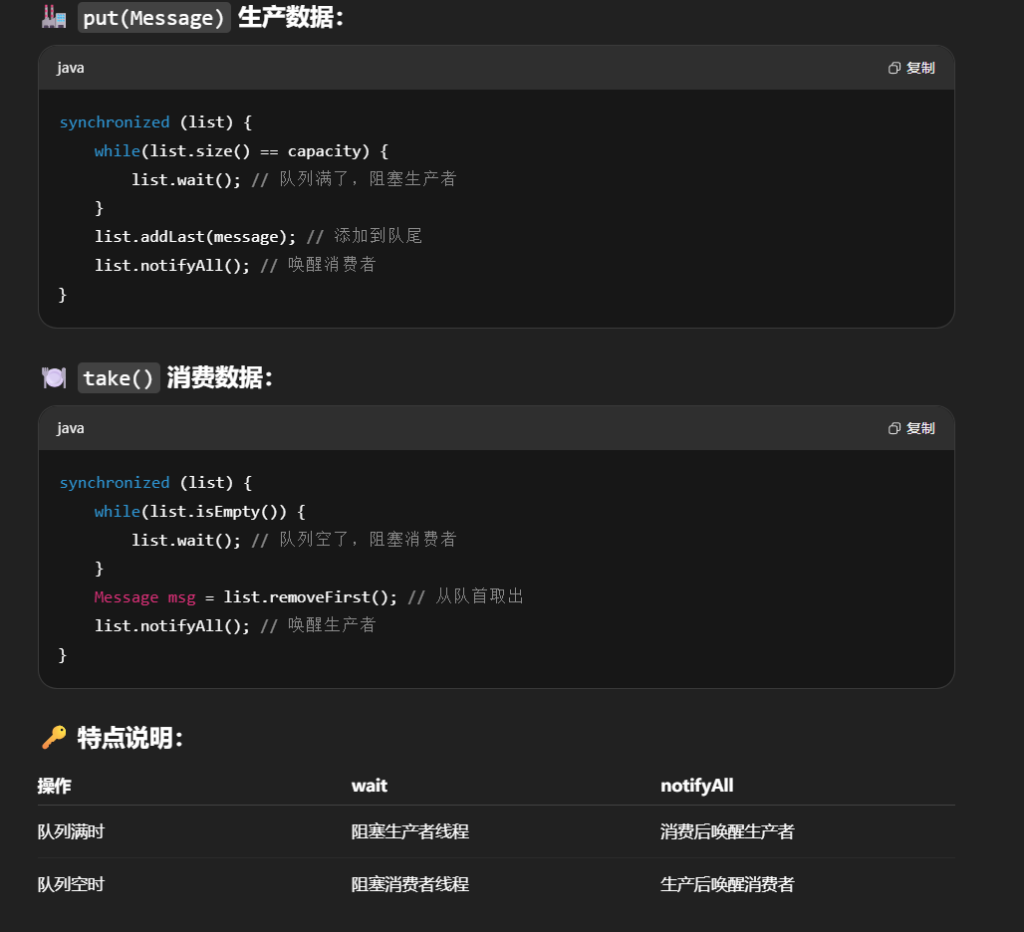
线程之间通信id很重要,线程之间不知道,id作为桥梁,可以检查消息受到了没有,因此设置一个Message类,在类里加入id属性。
在Message类前加final(不能有子类),仅有get方法,因此是线程安全的。
双向队列在Java里的实现是LinkedList

1 | @Slf4j(topic = "c.Test21") |
测试
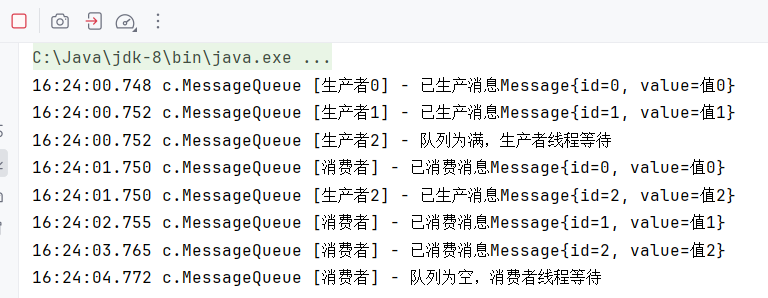
你可以看到:
- 队列容量设为 2,前两个生产者插入成功
- 第三个生产者等待
- 消费者消费一个后唤醒等待的生产者
总结:为什么生产者消费者模式实用?
| 特点 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 异步解耦 | 生产和消费节奏可以不同步 |
| 队列限流 | 通过容量控制系统压力 |
| 支持多生产多消费 | 不需一一绑定 |
| 可用于管道式任务流 | 在并发任务中广泛应用(如线程池、任务队列) |
4.11Park & Unpark
接下来介绍LockSupport.park/unpark 的使用及其原理机制,这是实现线程挂起与唤醒的底层工具
基本使用
LockSupport 是 Java 提供的工具类,用于精细控制线程的 阻塞(park) 与 唤醒(unpark)。
1 | // 暂停当前线程 |
park()会让当前线程进入“休眠”状态;unpark(thread)可以让某个线程恢复运行;- 它们可以先
unpark(),后park(),这点区别于wait/notify。
两种调用顺序对比
1.先 park 再 unpark
1 | Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { |
输出
1 | 18:42:52.585 c.TestParkUnpark [t1] - start... |
- t1 先调用
park(),进入休眠 - 主线程稍后调用
unpark(t1),t1 醒来执行
先 unpark 再 park
1 | Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { |
输出
1 | 18:43:50.765 c.TestParkUnpark [t1] - start... |
- 主线程先调用
unpark(t1),给 t1 一张“通行证” - t1 后来
park()检查到自己已“持票”,直接继续执行,不阻塞
特点
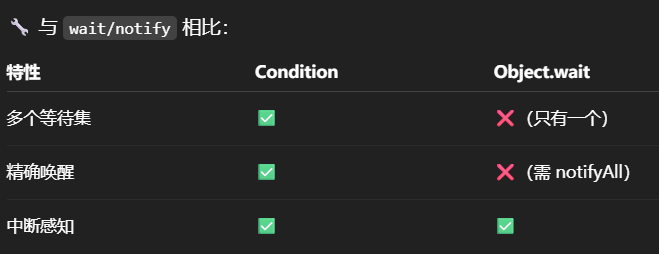
与Obeject的wait和notify相比:
1.wait,notify和notifyAll必须配合Object Monitor一起使用(也就是要先给对象上锁),而park和unpark不必。
2.park和unpark是以线程为单位来阻塞和唤醒线程,而notify只能随机唤醒一个等待线程,notifyAll是唤醒所有等待线程,不那么精确。
3.park和unpark可以先unpark,而wait和notify不能先notify。
| 特性 | wait/notify | park/unpark |
|---|---|---|
| 是否需要锁支持 | ✅ 需要在 synchronized 中 | ❌ 不需要 |
| 唤醒粒度 | 随机唤醒一个或所有线程 | ✅ 精确指定线程唤醒 |
| 调用顺序限制 | 必须先 wait 再 notify | ✅ 支持先 unpark 后 park |
| 性能和控制 | 较复杂 | ✅ 更灵活、更底层 |
原理
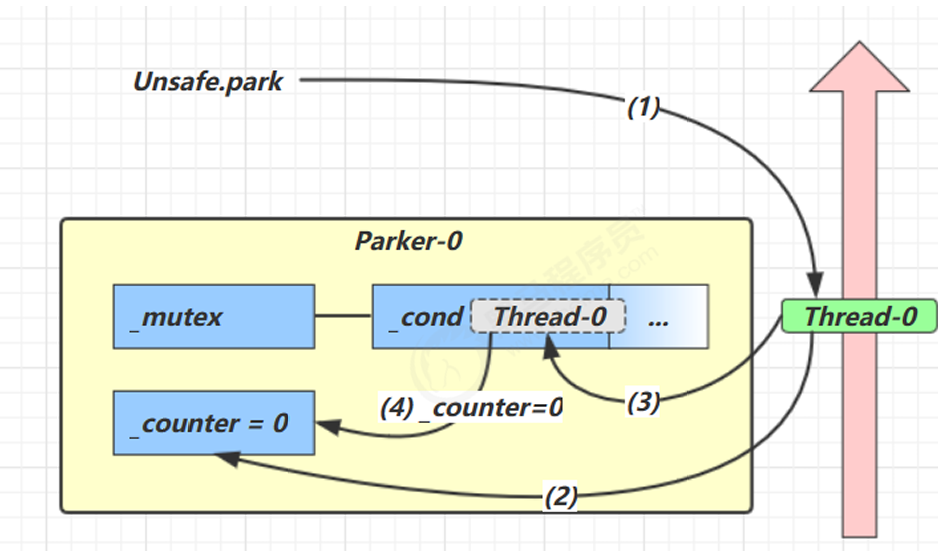
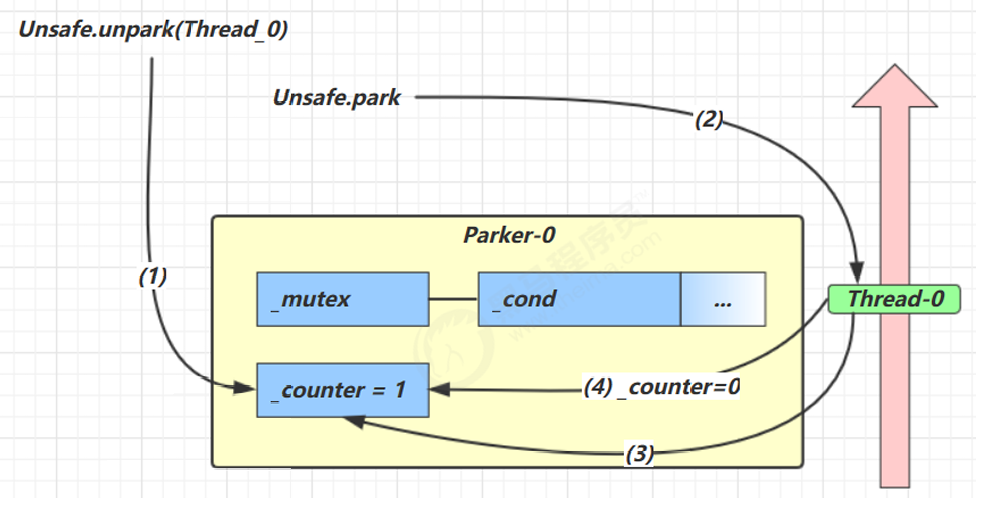
每个线程都有自己的一个 Parker 对象(由C++编写,java中不可见),由三部分组成 _counter, _cond和 _mutex 打个比喻
线程就像司机开的车。
| 组成部分 | 含义类比 |
|---|---|
_counter |
汽油量(0=没油,1=有油) |
_cond |
加油站队列(条件变量) |
_mutex |
排队用的锁(互斥锁) |
情况1:正常 park(线程主动休眠)
类比:司机发现没油,排队进加油站,等待别人来加油(unpark)
当前线程调用Unsafe.park()方法。检查_counter,本情况为0,代表汽油不足,此时就会获得互斥锁。线程就像司机开的车要进入_cond加油,所以条件变量阻塞。再确保设置_counter=0。
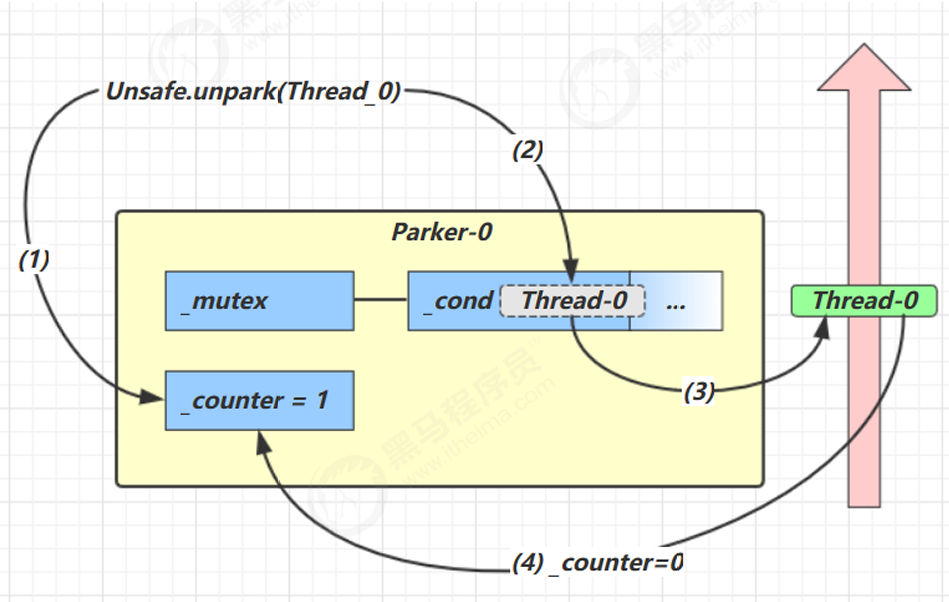
情况2:unpark 之后唤醒
类比:加油员加完油,通知排队司机可以继续上路
调用unpark之后,首先会把_counter置为1,代表汽油补充完毕。然后会唤醒_cond中等待的变量。然后该线程恢复运行。最后会设置_counter为0。
情况3:unpark 在前(先加油)
有人偷偷帮你加了油,司机后来发现油满,不用再排队加油,直接开走
如果先调用unpark,相当于给汽车加油,设置_counter为1。然后调用park方法,此时会检查_counter会发现_counter为1,相当于汽车有油,此时不需要加油,汽车继续上路。最后会把counter置为0,代表汽车上路油逐步会消耗完。
park & unpark 使用技巧
| 建议 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 替代 wait/notify | 更灵活、更底层,不需要锁 |
| 使用 while 循环 | 避免虚假唤醒(推荐) |
| park 不一定阻塞 | 如果之前 unpark 了,相当于获得通行证 |
| 一次 unpark 对应一次 park | 多余的 unpark 不会累计 |
4.12线程状态转换
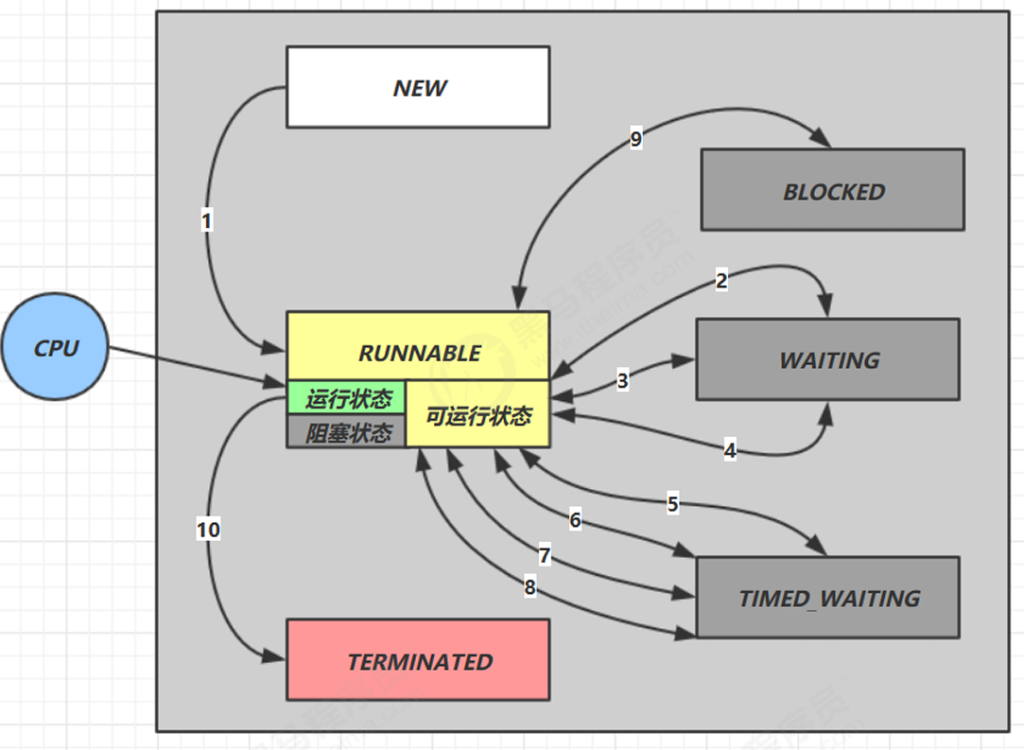
Java 线程生命周期全览
Java 中线程有如下 6 种状态(定义于 Thread.State):
| 状态 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| NEW | 新建状态(还未启动) |
| RUNNABLE | 就绪/运行状态 |
| BLOCKED | 阻塞状态(等待锁) |
| WAITING | 无限等待(需其他线程显式唤醒) |
| TIMED_WAITING | 有时间限制的等待 |
| TERMINATED | 线程运行完毕或异常终止 |
假设有线程 Thread t
情况 1 NEW --> RUNNABLE
1 | Thread t = new Thread(); |
- 当线程对象调用
start(),线程就绪并交由 CPU 调度,状态变为RUNNABLE。
情况 2 RUNNABLE <--> WAITING
t 线程用 synchronized(obj) 获取了对象锁后
1 | synchronized(obj) { |
调用
obj.wait()方法时,会释放锁,并将线程t挂起进入 WAITING 状态。调用 obj.notify(),obj.notifyAll(),t.interrupt()时
- 竞争锁成功,t 线程从
WAITING --> RUNNABLE - 竞争锁失败,t 线程从
WAITING --> BLOCKED
- 竞争锁成功,t 线程从
1 | public class TestWaitNotify { |
TestWaitNotify 是一个典型的 等待-唤醒机制 的演示。
1 | Thread t1, t2 在 obj 上 wait(); |
t1、t2会进入 WAITING 状态notifyAll()唤醒两者后,只有一个能抢到锁 → RUNNABLE- 另一个将进入 BLOCKED
情况 3 RUNNABLE <--> WAITING(join)
1 | t.join(); |
- 当前线程调用
t.join()方法时,当前线程从RUNNABLE --> WAITING注意是当前线程在t 线程对象的监视器上等待 - t 线程运行结束,或调用了当前线程的 interrupt() 时,当前线程从
WAITING --> RUNNABLE
情况 4 RUNNABLE <--> WAITING(LockSupport)
1 | LockSupport.park(); |
- 当前线程调用
LockSupport.park()方法会让当前线程从RUNNABLE --> WAITING - 调用
LockSupport.unpark(目标线程) 或调用了线程 的interrupt(),会让目标线程从WAITING --> RUNNABLE
情况 5 RUNNABLE <--> TIMED_WAITING(wait 超时)
t 线程用 synchronized(obj) 获取了对象锁后
1 | obj.wait(n);//等待最多n秒后恢复。 |
调用
obj.wait(long n)方法时,t 线程从RUNNABLE --> TIMED_WAITINGt 线程
等待时间超过了 n 毫秒,或调用 obj.notify(),obj.notifyAll(),t.interrupt()
时
- 竞争锁成功,t 线程从
TIMED_WAITING --> RUNNABLE
- 竞争锁成功,t 线程从
- 竞争锁失败,t 线程从
TIMED_WAITING --> BLOCKED
情况 6 RUNNABLE <--> TIMED_WAITING(join 超时)
1 | t.join(1000);//当前线程等待目标线程最多 1 秒。 |
- 当前线程调用
t.join(long n)方法时,当前线程从RUNNABLE --> TIMED_WAITING注意是当前线程在t 线程对象的监视器上等待 - 当前线程等待时间超过了 n 毫秒,或t 线程运行结束,或调用了当前线程的
interrupt()时,当前线程从TIMED_WAITING --> RUNNABLE
情况 7 RUNNABLE <--> TIMED_WAITING(sleep)
1 | Thread.sleep(1000); |
- 当前线程调用
Thread.sleep(long n),当前线程从RUNNABLE --> TIMED_WAITING - 当前线程等待时间超过了 n 毫秒,当前线程从
TIMED_WAITING --> RUNNABLE(时间结束自动回到 RUNNABLE。)
情况 8 RUNNABLE <--> TIMED_WAITING(parkNanos)
1 | LockSupport.parkNanos(1000_000); |
- 当前线程调用
LockSupport.parkNanos(long nanos)或LockSupport.parkUntil(long millis)时,当前线程从RUNNABLE --> TIMED_WAITING(当前线程进入限时等待状态。) - 调用
LockSupport.unpark(目标线程) 或调用了线程 的interrupt(),或是等待超时,会让目标线程从TIMED_WAITING--> RUNNABLE(可被唤醒或超时。)
补充:parkNanos
这是 LockSupport 提供的一种 限时阻塞当前线程 的方法,单位是纳秒(1 纳秒 = 10⁻⁹ 秒)。
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
park() |
无限期阻塞,等待 unpark() |
parkNanos(long nanos) |
最多阻塞 nanos 纳秒 |
parkUntil(long deadline) |
阻塞到指定时间(毫秒时间戳) |
情况 9 RUNNABLE <--> BLOCKED(抢锁失败)
1 | synchronized(obj) { |
- t 线程用
synchronized(obj)获取了对象锁时如果竞争失败,从RUNNABLE --> BLOCKED - 持 obj 锁线程的同步代码块执行完毕,会唤醒该对象上所有
BLOCKED的线程重新竞争,如果其中 t 线程竞争 成功,从BLOCKED --> RUNNABLE,其它失败的线程仍然BLOCKED(被释放 → BLOCKED 线程竞争 → 胜者进入 RUNNABLE。)
情况 10 RUNNABLE <--> TERMINATED
1 |
|
- 当前线程所有代码运行完毕,进入
TERMINATED(线程完成所有任务或抛出未捕获异常都会结束生命周期。)
总结:线程状态切换口诀
| 状态切换 | 条件 |
|---|---|
| NEW → RUNNABLE | 调用 start() |
| RUNNABLE → BLOCKED | 等待锁时失败 |
| BLOCKED → RUNNABLE | 拿到锁 |
| RUNNABLE → WAITING | wait()、join()、park() 等无限等待 |
| WAITING → RUNNABLE | notify()、unpark()、interrupt() 等唤醒 |
| RUNNABLE → TIMED_WAITING | sleep()、wait(1000)、join(1000) |
| TIMED_WAITING → RUNNABLE | 超时、被唤醒 |
| 任意 → TERMINATED | run 方法执行完毕或抛出异常 |
4.13优化手段:多把锁(细粒度锁)
1.什么是“多把锁”?
如果多个任务之间互不干扰,可以为它们准备不同的锁对象,从而同时执行,提升并发度。
2.场景类比:大屋子问题
有一间大屋子(类 BigRoom)具备两个功能:
- 睡觉(sleep)
- 学习(study)
❌ 错误设计:只用一把锁(this)
1 | public void sleep() { |
结果:
- 小南要学习,小女要睡觉
- 学习线程先抢到锁,睡觉线程只能等
- 虽然两个行为没关系,但它们被“串行”了!
1 | 12:13:54.471 |
3.正确设计:多把锁(细粒度)
1 | private final Object studyRoom = new Object(); |
结果:
- 小南学习锁住
studyRoom - 小女睡觉锁住
bedRoom - 两个操作并发执行,不互相等待
1 | 12:15:35.069 |
4.原理解析
| 对象锁选择 | 影响范围 | 并发度 |
|---|---|---|
synchronized(this) |
所有方法共用同一个锁 | 串行执行(竞争) |
| 多个锁对象 | 每个功能一把独立锁 | 并发执行(互不干扰) |
5.注意事项
避免一个线程获取多把锁
→ 例如 sleep() 里面还去 study(),容易造成 死锁。
细粒度锁仅用于互不相关的代码段
→ 如果 sleep 和 study 会同时访问共享资源,就不能这么干。
4.14线程的活跃性(3种现象)
什么是活跃性问题?
活跃性问题表示线程没有进入终止状态,看起来还在运行,但实际无法完成任务。
常见三类:
| 问题 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 死锁 | 多线程互相等待资源,不再运行 |
| 活锁 | 线程不断运行但无法前进 |
| 饥饿 | 某个线程长期得不到资源执行 |
其一活跃性 死锁现象
什么是死锁?
死锁:多个线程因相互等待对方释放资源而永久阻塞,程序进入“卡死”状态,无法继续执行下去。
有这样的情况:一个线程需要同时获取多把锁,这时就容易发生死锁
各自持有一把锁,但还想获得对方的锁:
1 | Object A = new Object(); |
分析:
- t1 拿了 A,睡了一会,想要 B
- t2 拿了 B,也想要 A
- 结果:双方都在等对方释放锁,永远卡住了
死锁成立的四个必要条件(操作系统理论)
| 条件 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 互斥(Mutual Exclusion) | 资源一次只能被一个线程使用 |
| 持有并等待(Hold and Wait) | 线程持有资源并申请新资源 |
| 不可抢占(No Preemption) | 已占有资源不可强行剥夺 |
| 循环等待(Circular Wait) | 多线程间形成资源的环形等待链 |
🚨 只要打破其中任意一个,就可以避免死锁
解决方式:
- ReentrantLock
定位死锁
检测死锁可以使用 jconsole工具/visualVM/Arthas,或者使用 jps 定位进程 id,再用 jstack 定位死锁:
1 | cmd > jps |
- 避免死锁要注意加锁顺序
- 另外如果由于某个线程进入了死循环,导致其它线程一直等待,对于这种情况 linux 下可以通过 top 先定位到 CPU 占用高的 Java 进程,再利用 top -Hp 进程id 来定位是哪个线程,最后再用 jstack 排查

经典死锁案例-哲学家就餐问题
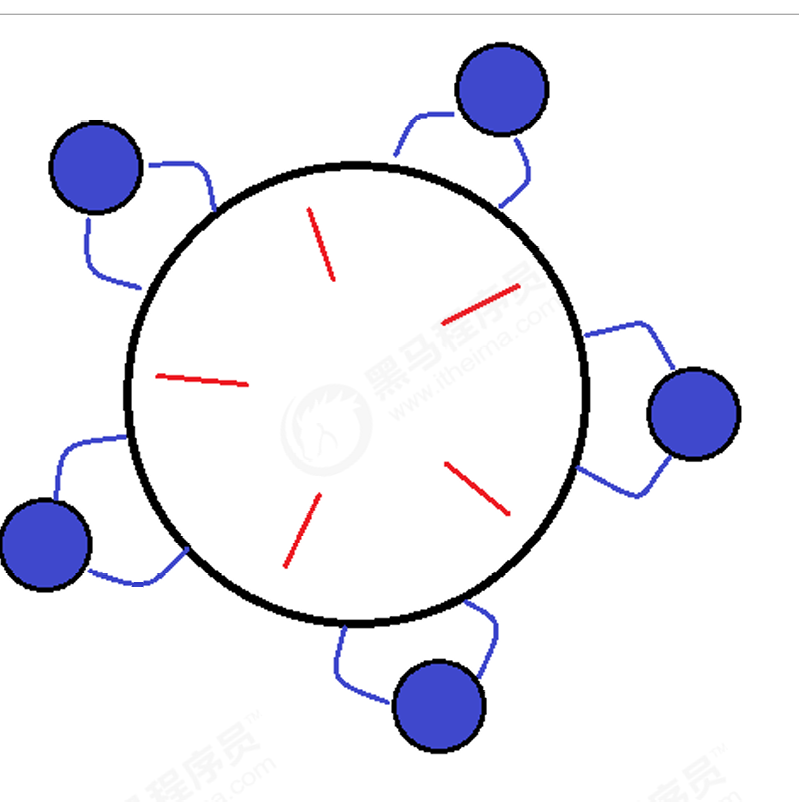
场景说明:
- 5 位哲学家围坐圆桌,思考与吃饭交替进行
- 每次吃饭要拿左右两根筷子
- 每根筷子只能被一人拿
- 如果大家都先拿左手筷子,再等右手筷子,就会导致死锁!
筷子类
1 | class Chopstick { |
哲学家类
1 | class Philosopher extends Thread { |
就餐
1 | Chopstick c1 = new Chopstick("1"); |
执行不多会,就执行不下去了
使用 jconsole 检测死锁,发现

在后面的讲解中我们会介绍ReentrantLock来解决死锁问题
这种线程没有按预期结束,执行不下去的情况,归类为【活跃性】问题,除了死锁以外,还有活锁和饥饿者两种情况
| 类型 | 表现 |
|---|---|
| 死锁 | 线程永远互相等待 |
| 活锁 | 线程不断让出资源,但始终抢不到锁 |
| 饥饿 | 某线程始终得不到执行机会(优先级过低或被饿死) |
其二活锁
概念
线程虽然没有阻塞(还能运行),但一直在“礼让”、“修正”,永远无法完成任务。
活锁出现在两个线程互相改变对方的结束条件,最后谁也无法结束,例如
1 | public class TestLiveLock { |
代码分析:
1 | // t1希望 count 减到 0 退出 |
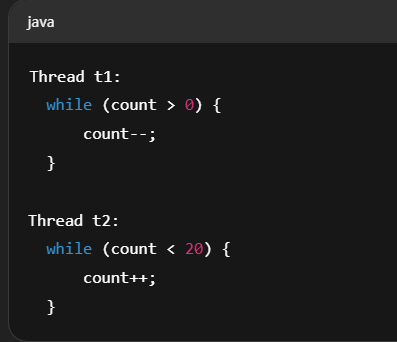
问题:
- t1 减一,t2 马上加一
- t1 永远达不到 count == 0,t2 永远达不到 count == 20
- 它们在“帮倒忙”,互相改变条件,陷入无尽循环
解决方式:错开节奏 → 打破交替循环
将睡眠时间调整为随机数。
1 | // 引入随机睡眠时间 |
目的:
- 打破同步
- 避免你加我减的“对撞”
- 让某一方有机会先完成目标
其三饥饿
概念
某个线程因为资源(如锁)长期被别的线程占用,得不到调度执行。
原因:
| 情况 | 举例 |
|---|---|
| 线程优先级过低 | 永远得不到 CPU |
| 被其它线程“霸占”资源 | 其它线程频繁获得锁,某线程永远等不到 |
| 不公平锁机制 | 锁不保证“先来先得” |
下面我讲一下我遇到的一个线程饥饿的例子,先来看看使用顺序加锁的方式解决之前的死锁问题
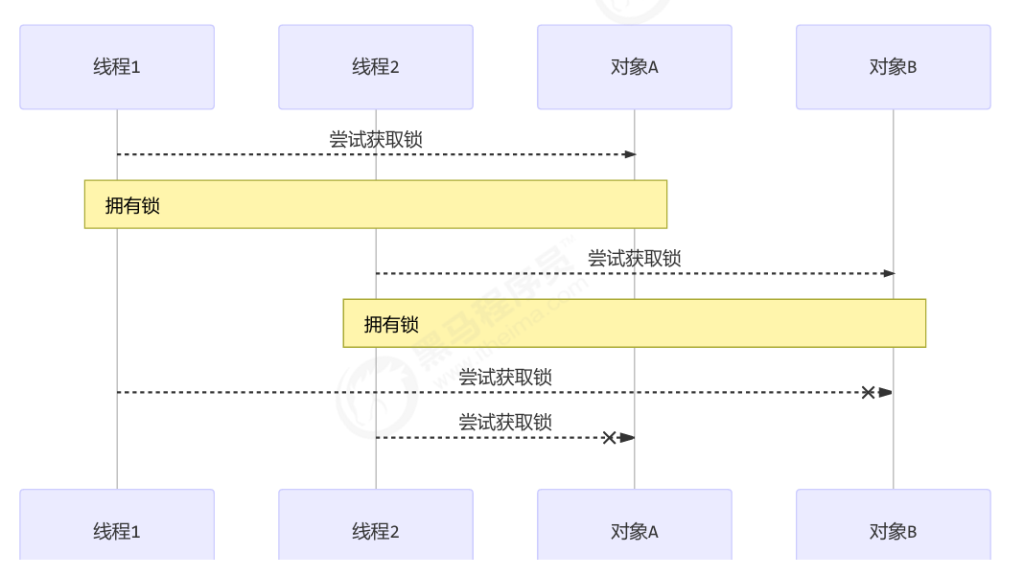
- 所有线程必须按顺序加锁 A→B→C
- 某些线程总是抢不到锁(因为其他线程一直先到)
- 这些“慢线程”就会“饿死”,迟迟得不到资源
顺序加锁可以解决死锁问题,但也会导致一些线程一直得不到锁,产生饥饿现象。
顺序加锁的解决方案
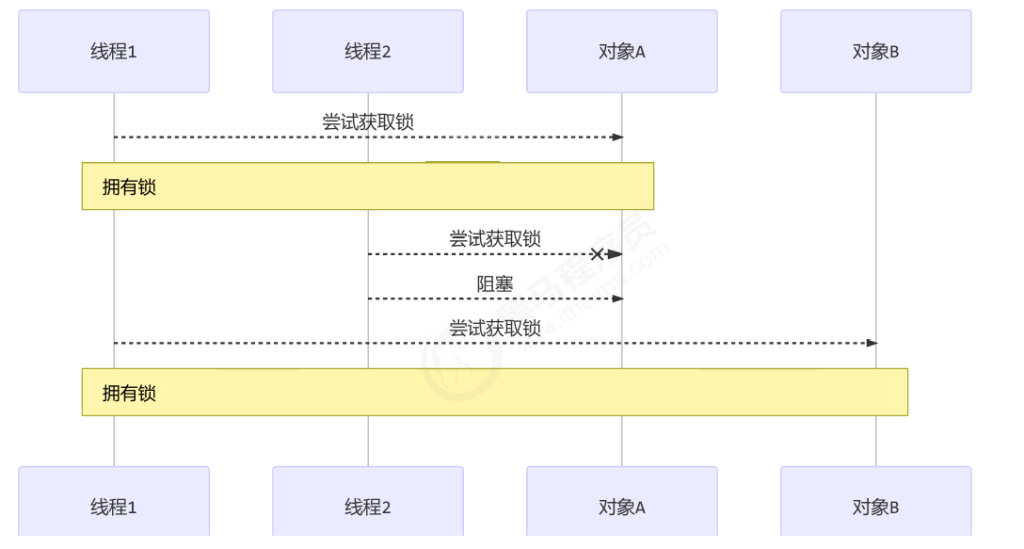
说明:
解决方式:ReentrantLock
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 使用 ReentrantLock + 公平锁 | new ReentrantLock(true) |
| 控制锁的占用时间 | 限时加锁(tryLock + timeout) |
| 增加线程优先级 | 或使用线程调度策略 |
死锁 vs 活锁 vs 饥饿 对比总结
| 比较项 | 🧱 死锁 | 🔁 活锁 | 🥀 饥饿 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 是否运行 | ❌ 不再运行(卡住) | ✅ 一直运行 | ❌ 可能未运行(得不到调度) |
| 是否能得锁 | ❌ 相互等待对方释放 | ✅ 可以反复得锁但没前进 | ❌ 一直得不到锁 |
| 是否释放锁 | ❌ 不释放 | ✅ 频繁让出资源 | ❌ 没机会获取资源 |
| 是否礼让他人 | ❌ 否 | ✅ 是(你先来我再来) | ❌ 否 |
| 是否能检测 | ✅ JVM可检测 | 🟡 较难检测 | 🔴 非常难检测 |
| 是否主动退出 | ❌ 永久阻塞 | ❌ 没有明确退出条件 | ❌ 被动等待资源 |
口诀:
三兄弟,三种死法:
- 死锁:线程你等我,我等你,一起凉;
- 活锁:你先来我先来,转圈圈白忙活;
- 饥饿:没人理我,永远得不到资源吃饭!
4.15ReentrantLock
Reentrant 表示可重入,ReentrantLock表示可重入锁。
ReentrantLock 是 JUC(java.util.concurrent)包中的可重入锁,它提供了比 synchronized 更灵活的加锁与解锁方式。
相对于 synchronized 它具备如下优势
| 特性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ✅ 可中断 | 阻塞线程可被 interrupt() 唤醒 |
| ✅ 可限时尝试加锁 | tryLock() 尝试获取锁 |
| ✅ 支持公平锁 | 可设置公平策略,先来先得 |
| ✅ 支持多条件变量 | 可用 Condition 实现多个等待队列 |
| ✅ 可重入 | 同一个线程可以重复加锁,不会死锁 |
与synchronized一样,都支持可重入(自己加的锁,没释放前,下一次还能进去)。
基本语法
1 | // 获取锁 |
务必记得用 finally 保证解锁!
可重入特性
可重入是指同一个线程如果首次获得了这把锁,那么因为它是这把锁的拥有者,因此有权利再次获取这把锁 如果是不可重入锁,那么第二次获得锁时,自己也会被锁挡住。
1 | static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); |
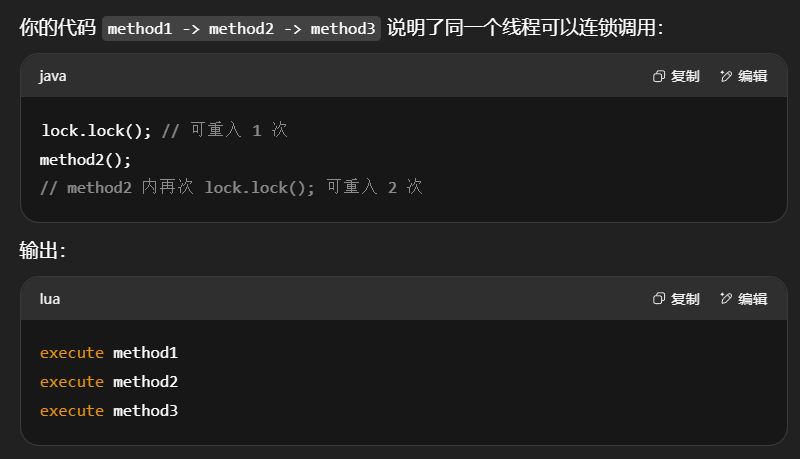
输出
1 | 17:59:11.862 [main] c.TestReentrant - execute method1 |
可打断
可打断指的是处于阻塞状态等待锁的线程可以被打断等待。注意lock.lockInterruptibly()和lock.trylock()方法是可打断的,lock.lock()不是。可打断的意义在于避免得不到锁的线程无限制地等待下去,防止死锁的一种方式。
示例
1 | ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); |
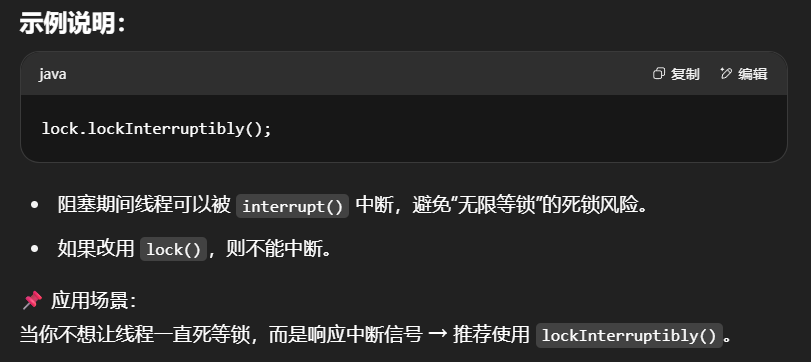
输出
1 | 18:02:40.520 [main] c.TestInterrupt - 获得了锁 |
注意如果是不可中断模式,那么即使使用了 interrupt 也不会让等待中断
1 | ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); |
输出
1 | 18:06:56.261 [main] c.TestInterrupt - 获得了锁 |
锁超时
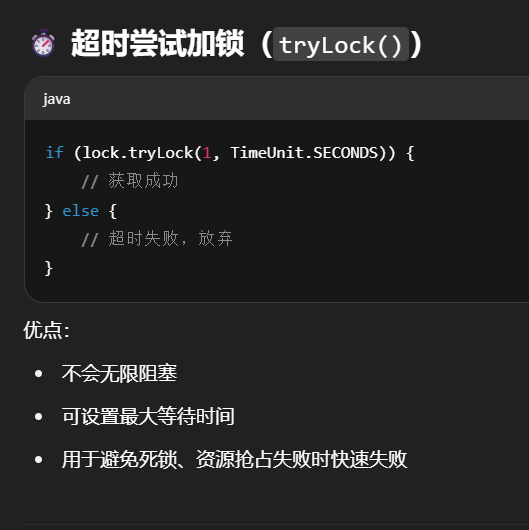
立刻失败
1 | ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); |
输出
1 | 18:15:02.918 [main] c.TestTimeout - 获得了锁 |
超时失败
1 | ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); |
输出
1 | 18:19:40.537 [main] c.TestTimeout - 获得了锁 |
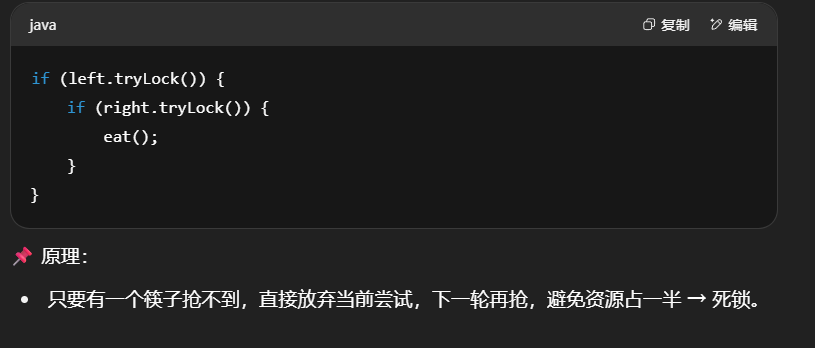
使用 tryLock 解决哲学家就餐问题
1 | class Chopstick extends ReentrantLock { |
公平锁
ReentrantLock 默认是不公平的
❓ 什么是“公平”?
- 公平锁:等待时间最长的线程优先获取锁 → 先到先得
- 非公平锁(默认):新线程可能插队获取锁 → 后来者有机会先执行
1 | ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(false); |
强行插入,有机会在中间输出
注意:该实验不一定总能复现
1 | t39 running... |
改为公平锁后
1 | ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true); |
强行插入,总是在最后输出
1 | t465 running... |
公平锁一般没有必要,会降低并发度,后面分析原理时会讲解

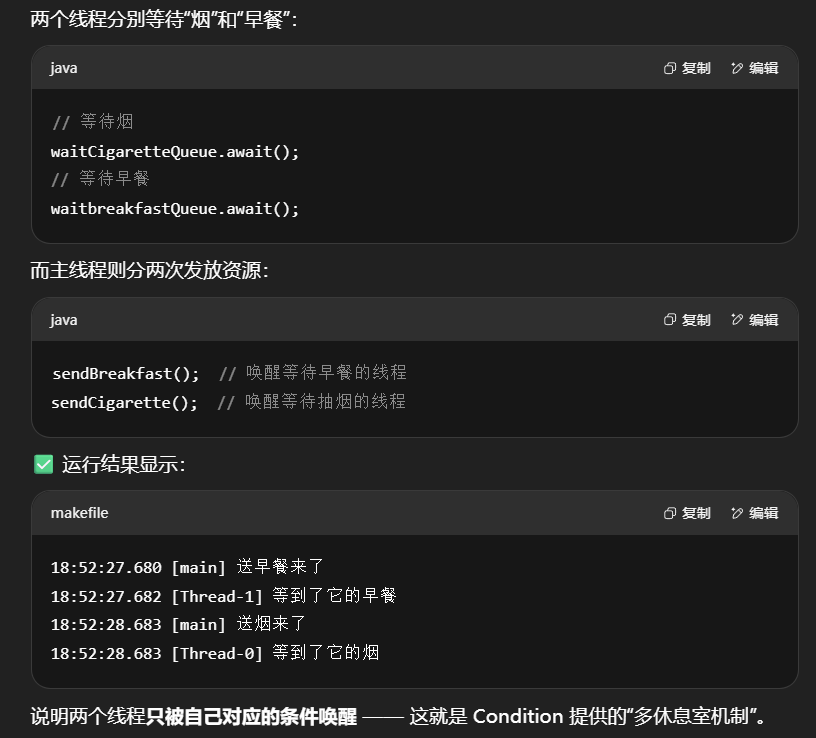
条件变量 Condition:多休息室模型
本质理解:
在 synchronized 中,所有等待线程都进入同一个“休息室”(waitSet),一旦 notify(),会唤醒任意一个,不管它想等啥。
而 ReentrantLock 提供了 多个条件队列(Condition),就像多个“等候区”:
- 等烟的线程放进
waitCigaretteQueue - 等早餐的线程放进
waitBreakfastQueue

使用要点
| 步骤 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 1️⃣ 创建多个 Condition | Condition cond = lock.newCondition(); |
| 2️⃣ await() 前必须加锁 | 否则抛异常 |
| 3️⃣ await() 会释放锁并进入 condition 队列 | |
| 4️⃣ 被 signal() 唤醒后,需重新抢锁,继续执行 |
例子
1 | static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); |
输出
1 | 18:52:27.680 [main] c.TestCondition - 送早餐来了 |
Condition 常见 API 概览
| 方法名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
await() |
当前线程进入等待(可中断) |
awaitUninterruptibly() |
不可中断地等待 |
awaitNanos(nanos) |
限时等待(纳秒) |
awaitUntil(Date) |
等到某个时间点 |
signal() |
唤醒一个等待线程 |
signalAll() |
唤醒所有等待线程 |
4.16同步模式之顺序控制
固定运行顺序
比如,必须先 2 后 1 打印
- wait notify 版**
wait+notifyAll
1 | // 用来同步的对象 |
原理说明:
t1线程一开始就等待标志位t2runedt2先输出 2,设置t2runed = true,然后唤醒t1t1判断条件满足后输出 1
优缺点:
| 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|
| 实现直观 | 需要共享对象 + 标志位 + notifyAll |
| 兼容性好 | 编写麻烦,易错(先wait再notify) |
2.Park Unpark 版 LockSupport.park/unpark
以看到,实现上很麻烦:
- 首先,需要保证先 wait 再 notify,否则 wait 线程永远得不到唤醒。因此使用了『运行标记』来判断该不该 wait
- 第二,如果有些干扰线程错误地 notify 了 wait 线程,条件不满足时还要重新等待,使用了 while 循环来解决 此问题
- 最后,唤醒对象上的 wait 线程需要使用 notifyAll,因为『同步对象』上的等待线程可能不止一个
可以使用 LockSupport 类的 park 和 unpark 来简化上面的题目:
1 | Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { |
原理总结:
unpark()可以先于park()调用,照样有效(类似先发放通行证)park()阻塞线程,unpark()唤醒线程- 不再需要 synchronized、标志变量、while 检查
结论:在控制先后顺序的小范围协作上,LockSupport 更优雅、轻量
线程交替交替输出
线程 1 输出 a 5 次,线程 2 输出 b 5 次,线程 3 输出 c 5 次。现在要求输出 abcabcabcabcabc 怎么实现
wait notify 版 wait + notifyAll
1 | class SyncWaitNotify { |
关键点:
- 通过
flag控制当前应打印哪一个字母 - 每个线程都检查自己的“flag是否匹配”,不匹配就 wait()
- 打印完后切换 flag,然后
notifyAll()唤醒其他等待线程
优缺点:
| 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|
| 使用原生 JDK 支持 | notifyAll 开销大,可能会唤醒无关线程 |
| 可灵活扩展 | 代码略复杂、条件判断冗余 |
Lock 条件变量版``ReentrantLock + Condition
1 | class AwaitSignal extends ReentrantLock { |
机制说明:
- 每个线程持有自己的
Condition对象,类似“单独的休息室” - 当前线程打印后
signal()唤醒下一个线程的Condition
注意
该实现没有考虑 a,b,c 线程都就绪再开始
Park Unpark 版 LockSupport.park/unpark
1 | class SyncPark { |
原理说明:
- 每个线程打印后唤醒下一个
- 初始时由
main手动调用一次unpark(第一个线程) - 简洁、直观、不需要加锁
三种方式对比总结
| 特性 | wait/notify |
Condition |
LockSupport |
|---|---|---|---|
| 编写复杂度 | 中 | 高(结构清晰) | 最低 |
| 唤醒粒度 | 粗(notifyAll) | 精确(signal) | 精确(unpark) |
| 多线程配合 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 |
| 初学者推荐 | ✅ | ❌(需熟练掌握 Lock) | ✅ |
4.17 第四章小结
synchronized互斥保护临界区的代码不会因为线程上下文切换导致交错。
wait/notify同步是让条件不满足时线程等待。
lock:可打断、锁超时、公平锁、条件变量。

✅ 1. synchronized vs wait/notify vs Lock 对比表
| 特性 | synchronized |
wait/notify |
ReentrantLock + Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 是否可重入 | ✅ | ✅(与synchronized配合) | ✅ |
| 是否可中断 | ❌ | ✅(wait 可中断) | ✅(lockInterruptibly) |
| 是否可限时加锁 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅(tryLock) |
| 是否支持公平锁 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅(构造函数传 true) |
| 是否支持多条件变量 | ❌(只能一个 waitSet) | ❌ | ✅(多个 Condition) |
| 使用难度 | ⭐(初学者友好) | ⭐⭐(需配合 notifyAll) | ⭐⭐⭐(灵活、控制精细) |
✅ 2. 三种线程顺序控制方式对比
| 实现方式 | 原理 | 是否支持精确唤醒 | 实现复杂度 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
wait/notify |
条件+锁 | ❌(需 notifyAll) | 中 | 顺序执行、互斥等待 |
Condition |
多条件变量 + signal | ✅ | 高 | 多线程精准协作 |
LockSupport |
park/unpark“通行证机制” | ✅ | 低 | 轻量顺序控制 |
✅ 3. 活跃性问题对比表(死锁、活锁、饥饿)
| 问题类型 | 是否运行 | 是否能得锁 | 是否释放锁 | 是否可唤醒 | 是否可检测 | 特征表现 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 死锁 | ❌ 不运行 | ❌ 永远等资源 | ❌ 不释放 | ❌ | ✅ JVM可检测 | 线程互相等待,永不结束 |
| 活锁 | ✅ 运行 | ✅ 能拿锁但没用 | ✅ 不断释放 | ✅ | 🟡 较难 | 线程让来让去,无限循环 |
| 饥饿 | ❌ 不运行 | ❌ 一直抢不到锁 | ❌ 被“饿死” | ❌ | 🔴 极难 | 低优先级线程长期无调度机会 |
✅ 4. ReentrantLock 公平 vs 非公平
| 类型 | 是否插队 | 性能表现 | 是否常用 | 使用方式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非公平锁 | ✅ 可能插队 | 高 | ✅ 默认 | new ReentrantLock() |
| 公平锁 | ❌ 按顺序 | 低 | ❌ 较少 | new ReentrantLock(true) |